What Is Fileless Malware?
Fileless malware is a variant of computer-related malicious software that exists exclusively as a memory-based artifact, random-access memory (RAM) for example.
Fileless Malware Detection
What makes fileless infections so insidious is also what makes them so effective. There are also sayings that fileless malware is “undetectable”. This is not literally true; it just means that fileless infection is usually undetectable by antivirus, whitelisting, and other traditional endpoint security programs.
How to detect fileless malware? The fileless malware doesn’t write anything about its activity to the computer’s hard drives. Thus, it is very resistant to existing anti-computer forensic strategies that include hardware verification, pattern-analysis, signature detection, time-stamping, file-based whitelist, and so on.
Fileless malware leaves very little way of evidence that can be used by digital forensic investigators to identify illegitimate activity. As this kind of malware is designed to work in memory, it can persist on the operating system (OS) until the system is rebooted.
Fileless Malware Attacks
On Feb. 8, 2017, a report published by Kaspersky Lab’s Global Research and Analysis Team named “Fileless Attacks Against Enterprise Networks” involves in fileless malware and its newest variants. The report says that fileless malware infects about 140 enterprise networks all over the world including telecommunication enterprises, government organizations, and banks.
The report also shows how a fileless malware variant performs an attack against a target computer relying on PowerShell scripts, which locates within the Windows Registry. It leverages a common attack framework named Metasploit with supporting attack tools like Mimikatz and standard Windows utilities like “NETSH” and “SC” to assist with lateral movement.
This fileless malware was only found after a bank identified the Metasploit Meterpreter code running in physical memory on a central domain controller (DC).
Besides Kaspersky, many other computer security program companies also identified fileless malware, such as MacAfee, Symantec, Trend Micro, Cybereason…
Fileless Malware vs In-memory Malware
Sometimes, fileless malware is considered synonymous with in-memory malware for both of them implement their main functions without writing data to hard drives within the whole life of their operation.
Therefore, some people think this variant is nothing new but a redefinition of the well-known “memory resident virus”, whose pedigree can be traced back to the birth of the Lehigh Virus (in the 1980s) that was developed by the originator of the term, Fred Cohen, and became famous with his paper on the topic.
However, to be exact, the “fileless malware” is not the synonymy of “in-memory malware” though they have the same execution environment – system memory. They do have differentiation. The biggest difference between fileless malware and in-memory malware is the method of inception and prolongation.
Most malware’s infection vector will write something to the disks for itself to be executed. The origin of the malware can rely on the form of external media devices like USB flash drives, mobile phones, attachments, side-channel, browser drive-by, etc.
Either in-memory malware or memory-resident malware has to have contact with the hard disks in the host computer in some form or another. Therefore, even employing the stealthiest anti-forensic methods, some form of infected residue will be left on the hard drives.
Yet, as for fileless malware, from the inception until the termination (usually by system reboot), it aims never to write its contents on hard drives. Fileless malware aims to reside in volatile OS areas including in-memory processes, registry, as well as service areas.
How Does Fileless Malware Work?
Fileless malware is an evolutionary strain of virus that has taken on a steady model of self-improvement or self-enhancement with a drive towards clearly defined and focused attack scenarios. Its roots can be traced back to the memory-resident (terminate-and-stay-resident) virtual programs.
Once those virtual programs were launched, the fileless malware will reside in memory awaiting a system interrupt before getting access to their control flow. There are some fileless malware examples like The Dard Avenger, Number of the Beast, and Frodo.
Fileless Malware Common Technologies/Types
- Memory-only malware
- Registry resident malware
- Fileless ransomware
- Exploit kits
- Steal credentials
- Hijack native programs
Those technologies evolved by way of temporary memory-resident viruses; Monxla and Anthrax are famous for adopting those techniques. Those technologies take on their truer “fileless” nature by way of in-memory injected network worms or viruses like Slammer and CodeRed.
Fileless Malware Attack Process
Fileless attacks belong to low-observable characteristics (LOC) attacks, which is a type of stealth attack that evades detection by most anti-malware and frustrates forensic analysis efforts. Instead of working in common hard drive files, fileless malware operates in computer memory.
Without directly installing on the host or being contained in a file, fileless viruses directly go into system memory. By hacking PowerShell, it can access just about anything in Windows.
Below is an example process for fileless attack:
Step 1. User clicks on a link in spam email.
Step 2. Website loads flash and triggers exploit.
Step 3. Shellcode runs PowerShell with CMD line to download and execute the payload in memory only.
Step 4. Download an in-memory execution and reflectively load code. The payload can perform exfiltration, damage, etc.
Step 5. Create an auto-start registry to invoke PowerShell with a CMD line.
Fileless Malware Spreading Process
Fileless attacks are typically used for lateral movement. They spread from one computer to another to obtain access to valuable data across the enterprise network.
To avoid suspicion, fileless malware goes into the inner parts of trusted and whitelisted processes such as PowerShell, wscript.exe, and cscript.exe or the OS itself to implement malicious processes. Most automated malware scans can’t detect command line changes. Although a trained analyst can identify those scripts, he usually does not know where to check for them.
Step 1. Get access by remotely exploiting a vulnerability and using web scripting for remote access.
Step 2. Steal credentials in the same method.
Step 3. Maintain persistence by modifying the registry to create a backdoor.
Step 4. Steal data using the file system and built-in compression utilities. Then, upload data from the infected computer via FTP.
Fileless Malware Protection
How to Avoid Being Infected by Fileless Malware? Since fileless malware is hard to detect and therefore more difficult to remove, you’d better stop it from successfully attacking your machine and keep it out of your computer. Then, how to achieve that?
#1 Don’t Open Malicious Links and Files
Regarding the process of fileless attacks, one of the effective ways is to avoid clicking on unknown links from spam email or unsecured websites. Also, you’d better not open attachments from unknown senders.
#2 Keep Your Software Up to Date
Secondly, always keep your programs of the newest version is another way to defend against fileless attacks, especially for Microsoft applications.
#3 Use Security Programs and Firewall
If you can’t ensure computer security by yourself, you should rely on security solutions, either system built-in programs or third-party ones. No matter which one your select, you should make sure that it builds an integrated and multi-layered approach that addresses the entire threat lifecycle. Thus, you can investigate every phase of the campaign before, during, and after an attack.
- Be able to see and measure what is happening
- Control the state of the targeted system
How to Remove Fileless Malware?
Fileless malware is a kind of malware that makes use of legitimate applications to infect computers. It relies on no files and leaves no footprint. Thus, it is difficult to detect and remove the fileless malware.
#1 Rely on Powerful Security Software
Fileless malware has been effective in evading all but the most sophisticated security solutions, such as McAfee Endpoint Security, Norton 360, CrowdStrike, and Varonis. So, if you are unfortunately affected by fileless malware, you can choose one of them or another anti-malware to help you remove fileless malware.
#2 Reboot Windows
Also, just as described in the former part of this article, you can try to reboot your system to get rid of fileless malware.
#3 Clean System Memory
If you choose to clean computer memory to do fileless malware removal, you need to be prepared for a fresh start. Actually, just reset Windows to factory default settings or reinstall the system can help you rebuild your memory.
How to Save Data from Lost During Fileless Malware Attack?
Since it is difficult to detect and delete fileless malware once it gets into your computer, you should take some actions when you are still unaffected by fileless attacks. Besides the methods to avoid being infected by fileless malware mentioned above, another important task you need to complete is to back up vital files on your computer.
Once you have a backup of important files, even if you lose them while removing fileless malware by computer hard reset, you can still restore them from the backup image. To create a backup of crucial items, you are recommended to rely on a professional and reliable program such as MiniTool ShadowMaker.
Step 1. Download and install MiniTool ShadowMaker on your computer.
Step 2. Open it and click Keep Trial if you are asked to buy.
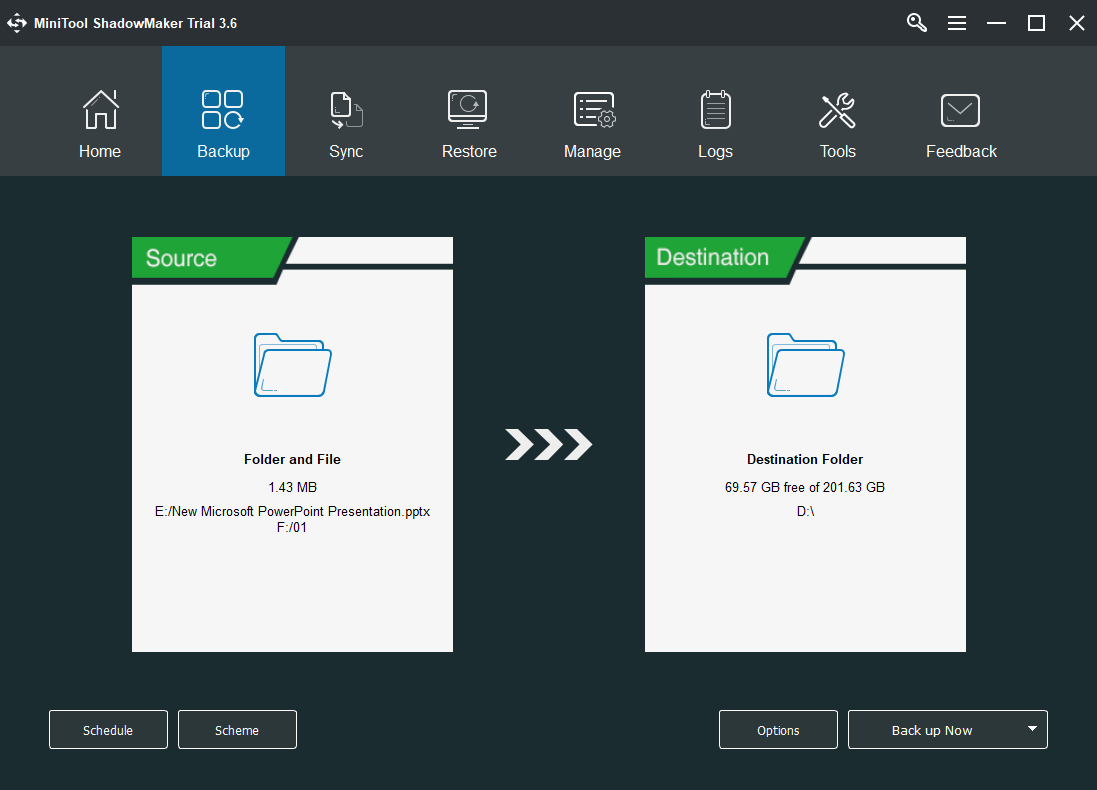
Step 3. Click Backup in the top menu of the main interface.
Step 4. Click the Source module in the Backup tab and select which files or programs you want to back up. You can also choose to back up the system, a partition/volume, or a whole hard drive.
Step 4. Click the Destination module to select where you’d like to store the backup image file. External storage space is recommended.
Step 5. Preview the backup process and confirm it by clicking the Backup up Now button.
It will pop up asking for your confirmation again, just approve it. Then, wait until it finishes or you can switch to other businesses while it is processing.
That is all about fileless malware. If you want to learn more related to fileless malware or attacks, you can view the below FAQ or search on this website; if you have any idea about fileless malware or other viruses, you can leave a comment below; if you come across any problem while using MiniTool ShadowMaker, feel free to contact via [email protected].