Hard Drives (HDDs)
Computers rely on hard drives (HDDs) to permanently store data. HDDs are storage devices for storing and retrieving digital information that will be referenced in the future. Maybe you are interested in this post – What Is Hard Disk? Comparisons Among SSD, HDD, and SSHD.

Hard drives have stood the test of time. The hard drive was released by IBM in 1956 and they were used in general-purpose mainframes and small computers at the times. Over these years, they have witnessed many technological advances. These innumerable changes allow HDDs to be retained, unlike other devices that are outdated when they are launched on the market.
If you want to buy an HDD for your computer and laptop, you had better have a basic knowledge of it since there are different types of hard drives. Thus, in the next part, I will introduce the details of the types of hard drives and you can know which one you should choose.
Types of Hard Drives
- Parallel ATA (PATA)
- Serial ATA (SATA)
- Small Computer System Interface (SCSI)
- Solid State Drives (SSD)
Types of Hard Drives
At present, we can divide the hard disk into four types – Parallel ATA, Serial ATA, Small Computer System Interface, Solid State Drives. Following is the information about them respectively.
Parallel ATA (PATA)
Parallel ATA (PATA) drives are one of the hard drive types. They are also known as integrated drive electronics (IDE) or enhanced integrated drive electronics (EIDE) drives. It is the first hard drive connected to a computer using the PATA interface standard.

The PATA drive was developed by Western Digital in 1986. It provides a driver with a common interface, which can be used on different devices commonly at the time. PATA drives can provide data transfer rates up to 133 MB/s. In the master/slave configuration, two PATA drives can be connected with one cable.
Up to four PATA drives can be connected to a single motherboard because most motherboards have two channels for IDE connections. Maybe you are interested in this post – [2020 Guide] How to Choose a Motherboard for Your PC.
However, the issue of PATA drives is that they are outdated. If you walk into any computer store today, it may not be possible to find any PATA drives.
Serial ATA (SATA)
As one of the HDD types, Serial ATA (SATA) hard drives are still considered to be the most common type of hard drives used today. It almost supports all computer motherboards and operating systems. SATA drives are usually one of two sizes: 3.5-inch hard drives for desktop computers and 2.7-inch small hard drives for laptop computers.

The disk of the SATA drive rotates at different speeds according to the model purchased. The speed can reach 10,000 RPM to increase data transmission. Storage devices used in large servers can even reach 15,000 RPM. However, higher RPM SATA drives are also more prone to failure. Actually, mechanical failure is one of the main disadvantages of SATA drives.
Small Computer System Interface (SCSI)
Small Computer System Interface is also one of the types of hard disk. It was developed in the 1970s and was first called Shugart Associates System Interface (SASI) after the company founded it. It uses a 50-pin flat ribbon connector to connect hard drives and other peripherals to the computer.
With standard interface technology, 7 to 15 devices are allowed to connect to a single motherboard. Although it is generally believed that SCSI is outdated, the SCSI can still be found in some low-end computers. Modern SCSI cables can transfer data at up to 80 MB/s.
Solid-State Drives (SSD)
One of the hard drive types is the solid-state drive (SSD). Today, it is at the forefront of storage technology development. It is a storage drive composed entirely of memory chips, rather than rotating magnetic disks in traditional hard disks.
The SSD does not have rotating disks or any other moving parts. Instead, the data in the SSD is stored in the semiconductor chip. SSDs work using the concept of flash memory, which is the same concept used in the random access memory (RAM) of the motherboard.
SSD lacks mobile components, thus, the SSD’s operating power consumption is greatly reduced. It’s one of the advantages of SSD. Another advantage of SSD is that it is not prone to failure. However, the biggest disadvantage of SSD is the price. With the same storage space, the cost of SSD is three to four times that of SATA hard drives.
Which One Should You Choose?
All types of hard drives have been introduced below. If you are confused among these hard drives and don’t know which one you should choose, keep on your reading to find the answer.
Storage Space
If you need large-capacity storage space, it is recommended to buy SATA. For example, the price of a Western Digital 1 TB HDD is less than $ 50. The cost of SSDs of the same size for the same brand is close to $ 200. But you need to notice that the data transmission and loading time in the hard drive is restricted, and this limitation may be insurmountable now.
Performance
If you want the system to start faster and the load time is greatly reduced, then it is best to invest in SSDs. SSDs are also less prone to failure due to mechanical damage or exposure to strong magnets. But, SSD is expensive.
Hybrid Option
Many data centers and computers for industrial use have adopted a hybrid approach that takes advantage of the best features of SSDs and HDDs. You can use traditional hard drives to store images, videos, documents, and files being processed. Then, you can use the SSD to exclusively store the operating system.
Maybe you already have an HDD and you may ask – what type of hard drive do I have?, then, you can refer to this post – What Hard Drive Do I Have Windows 10? Find Out in 5 Ways to find the answer. If you want to migrate HDD to SSD, you can go to the next part.
How to Migrate HDD to SSD
If you need faster performance and have installed Windows system on an HDD, then there is a method for you to migrate HDD to SSD without reinstalling the system. That is, use the free backup software – MiniTool ShadowMaker to do that.
It is a professional backup program that can be used to back up the operating system, disk, partition, file, and folder. Besides, it is a user-friendly program to protect your computer and data.
MiniTool ShadowMaker supports almost all storage devices that can be recognized by Windows, such as HDD, SSD, USB external disks, Hardware RAID, Network Attached Storage (NAS), Home File Server, and so on.
This backup software offers a Trial Edition that allows a 30-day free trial for all backup features. If you want to use it permanently, get its Pro Edition. Now you can download and try MiniTool ShadowMaker to back up your PC.
Now, let’s see how to migrate HDD to SSD step by step.
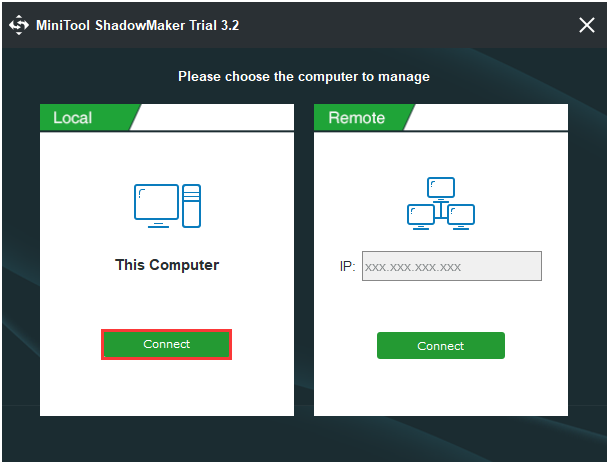
Step 1: Connect the SSD to your computer. Launch MiniTool ShadowMaker, click Keep Trial and click Connect in This Computer to continue.
Step 2: After entering the main interface, navigate to the Tools tab. And then choose the Clone Disk feature to continue.
Step 3: Next, you are required to choose the source disk and the target disk for cloning. Here, you intend to clone HDD to SSD, thus, please set the HDD as the source disk and SSD as the target disk.
Step 4: After you have successfully selected the disk clone source and destination, click OK to continue.
Step 5: Then you will receive a warning message that tells you all data on the target disk will be destroyed during the disk cloning process. Then click Yes to continue.
Step 6: Then it will begin to clone HDD to SSD and you need to wait several minutes until the process is finished.
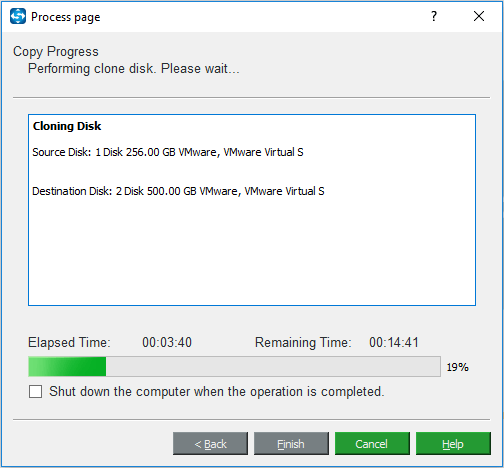
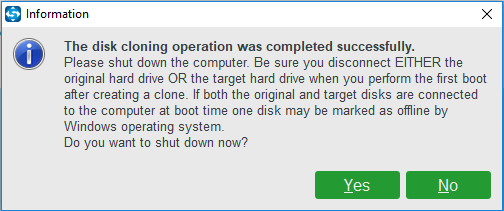
Step 7: When the disk clone process is finished, you will receive a message which tells you that the source disk and the target disk have the same signature. Thus, you need to remove the HDD from your computer and insert the SSD to the PC.
Also see: How to Upgrade Laptop from HDD to SSD Without Reinstalling OS
Bottom Line
In this post, you have got some information about the different types of hard drives. Also, you can know which one is better for your PC or laptop. Besides, if you want to clone HDD to SSD without reinstalling OS, MiniTool ShadowMaker is a helpful tool.
If you have any other ideas or any questions related to MiniTool software, please leave a comment or contact [email protected] and we will reply to you as soon as possible.
Types of Hard Drives FAQ
- Choose the correct interface.
- Choose the right capacity.
- Get a model with a large cache.
- Pay attention to power consumption and noise level.
- Length of warranty.
- MTBF.
- MTTR.