What Is a Cyber Attack?
What is a cyber-attack? Cyber-attack is a general description of a series of cyber activities, resorting to sorts of tools and techniques, to steal, expose, alter, or destroy data. Of course, as time goes by, hackers can carry out kinds of malicious operations on the Internet for beneficial intentions and vandalism.
Hackers have explored various methods to infiltrate victim’s systems. Sometimes, it can be developed to indiscriminate attack on the target and no one knows who will be the next victim.
There are three major motivations triggering the cybercriminals:
1. Criminally-motivated
Those attackers tend to seek money via theft or extortion. They can steal your data for business exchange, hack into a bank account to steal money directly, or extort victims.
2. Personally-motivated
Those hackers, normally, have specific targets to start the attack, such as their opponents. A personal grudge tends to be a major reason for this activity. Corporate espionage can steal intellectual property to gain an unfair advantage over competitors. Some hackers will exploit a system’s vulnerabilities to warn others about them.
3. Politically-motivated
Those hackers, mostly, are more skilled professionals. They can be trained and then involved in cyberwarfare, cyberterrorism, or hacktivism. The attacking targets focus on their enemies’ government agencies or critical infrastructure.
More or less, people may encounter some cyberattacks unwittingly. So, what are the common types of cyber-attacks? To help you better distinguish different types, the next part will illustrate them one by one.
Common Types of Cyber Attacks
Cyber attacks have been on the rise, with the digitization of business that has become more and more popular in recent years. There are dozens of types of cyber-attacks and we will list some common types that hassle people a lot.
Malware Attacks
Malware often appears as malicious software to carry out a series of untheorized actions on the victim’s system. The procedure is designed to cause harm to a computer, server, client, or computer network and infrastructure.
It is hard to notice these moves and according to their intentions and infiltrating methods, they can be categorized into some different types, including viruses, worms, Trojans, adware, spyware, ransomware, etc.
Those listed examples are the most common issues people may run into. Over the years with the high-speed development of electronic communications, it has become an attacking channel of new kinds, such as email, text, vulnerable network service, or compromised websites.
If you want to know how to identify the signs of malware on computers, this post will be helpful: What’s a Possible Sign of Malware on Computer? 6+ Symptoms.
Phishing Attacks
Phishing attacks often mean that your sensitive data, especially your usernames, passwords, credit card numbers, bank account information, etc., are exposed to hackers. They can utilize and sell that information for benefits. Most people are easily stuck into this pitfall because of unknown emails, links, or websites.
Spear-phishing Attacks
Phishing is a general term for cyberattacks carried out by email, SMS, or phone calls to scam masses of people, while if this attack has a specific victim target, we name it spear phishing. Those attacking channels are modified to specifically address that victim, which requires more thought and time to achieve than phishing.
Whale-phishing Attacks
Whale-phishing attack is a highly targeted phishing attack. Similar to the spear-phishing attack, it occurs when an attacker utilizes spear-phishing methods to go after a large, high-profile target, such as senior executives.
They can masquerade themselves as trusted entities so that victims can share highly sensitive information with a fraudulent account.
Distributed Denial-of-Service Attacks (DDoS)
The DDoS attack is one cyber attack that is designed to influence or overwhelm the availability of a target system by generating a large number of packets or requests. Similarly, a denial of service (DoS) attack can do the same thing to shut down a machine or network, making it inaccessible to its intended users.
These two attacks do have something different and if you want to learn about it, you can read this post: DDoS vs DoS | What’s the Difference and How to Prevent Them.
Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) Attacks
During this process, an attacker injects a malicious executable script into the code of a trusted application or website, then sends a malicious link to the user and tricks the user into clicking on the link to launch an XSS attack.
Then the transformed application or website will start the malicious link because of a lack of proper data sanitization, and then attackers can steal the user’s active session cookie.
Man-in-the-Middle (MITM) Attacks
As the name implies, a man-in-the-middle attack means that the attacker is in the middle of a conversation between a user and an application to eavesdrop the personal information. Normally, the hackers will set their targets to the users of financial applications, e-commerce sites, etc.
Botnets
Different from other attacks, botnets are computers that have been infected by malware and are under the control of attackers. Those botnet computers can be controlled to perform a series of illegal operations, such as stealing data, sending spam, and DDoS attacks.
The barrier to creating a botnet is also low enough to make it a lucrative business for some software developers. That’s why it has become one of the most common attacks.
Ransomware
Ransomware is malware that can infiltrate your system and encrypt your files to stop users’ access to files on their computers. Then hackers will demand a ransom payment for the decryption key. Alternatively, some ransom will lock the system without damaging any files until a ransom is paid.
SQL Injection Attacks
This attack can seek the web security vulnerability and utilize the code injection technique, to interfere with the queries that an application makes to its database. This kind of attack focuses on attacking the websites but can also be used to attack any type of SQL database.
Zero-Day Exploit
The zero-day exploit is a broad term to describe those attack activities in which hackers can take advantage of those security vulnerabilities to perform a system/web/software attack. Zero-day means that the victims or software vendor has no time to react and fix this flaw.
URL Interpretation
This kind of attack can also be called URL poisoning. Hackers often manipulate and modify the URL by altering the meaning while keeping the syntax intact. In this way, attackers can access and probe a web server and retrieve more information. This sort of attack is extremely popular with CGI-based websites.
DNS Spoofing
Domain Name Server (DNS) spoofing can trick people into a fraudulent, malicious website by manipulating DNS records. Sometimes, you may find your targeted website will be redirected to a new page that looks exactly like where you want to go.
However, it may be a pitfall set by hackers to induce you to log in to your genuine account and expose more sensitive information. They may seize the opportunity to install viruses or worms on your system, causing some unexpected results.
Brute Force Attacks
Brute force attacks mean that some person, it can be a stranger, hacker, or hostile, attempts to access the victim’s computer by trying all the passwords that they think the victim might set for the computer.
Normally, before they do that, hackers will track any clues on your social media and online information to deduce your password. So, do not expose your personal information to the public.
Trojan Horses
Trojan Horse often disguises itself as legitimate and harmless software, but once the virus gets activated, the Trojan virus can make cyber-criminals spy on you, steal your data, and access your system. If you want to know more about it, you can read this post: What Is a Trojan Virus? How to Perform Trojan Virus Removal.
How to Prevent Cyber-Attacks?
After knowing those common examples of cyber attacks, you may wonder how to prevent cyber-attacks effectively. There are some useful tips you may consider.
Tip 1: Keep Your Windows and Software Up to Date
It is necessary to keep your software and system up to date. Issued updates can not only provide advanced and brand-new features but also fix some system or software bugs and security issues detected in past tests. If you leave the update aside, hackers can find those weaknesses and seize the chance to infiltrate your system.
Tip 2: Install a Firewall
Windows has its built-in firewall and antivirus and you’d better keep the real protection on all the time. The features can better protect your computer from cyberattacks. However, is it enough to protect you against all the outside attacks? You may read this post for more information: Is Windows Defender Enough? More Solutions to Protect PC.
Apart from that, you can choose to install other reliable third-party antivirus or firewall to strengthen the protection shield.
Tip 3: Use Multi-Factor Authentication
What is a multi-factor authentication (MFA)? It is a core component of a strong identity and access management policy. During this login process, this MFA requires users to enter more information than just a password, which can protect personal data from being accessed by an unauthorized third party.
Tip 4: Back up Data Regularly
It is one of the most important steps to protect your important data – perform a regular backup. In the event of cyberattacks, you need your data backup to avoid serious downtime, loss of data, and serious financial loss.
Some people will forget to finish this task and think it is burdensome. Don’t worry. You may rely on this professional backup software – MiniTool ShadowMaker – to back up files, folders, partitions, disks, and your system.
Besides, it is worth trying the backup scheme and schedule settings to configure an automatic backup. You may set your automatic backup to start daily, weekly, monthly, or on event and try an incremental or differential backup to save your resources.
Download and install this program on your PC and try this for 30 days free.
MiniTool ShadowMaker TrialClick to Download100%Clean & Safe
Step 1: Launch the program and click Keep Trial to go on.
Step 2: In the Backup tab, click the SOURCE section to choose what you want to back up, and then go to the DESTINATION section to choose where to store the backup, including User, Computer, Libraries, and Shared.
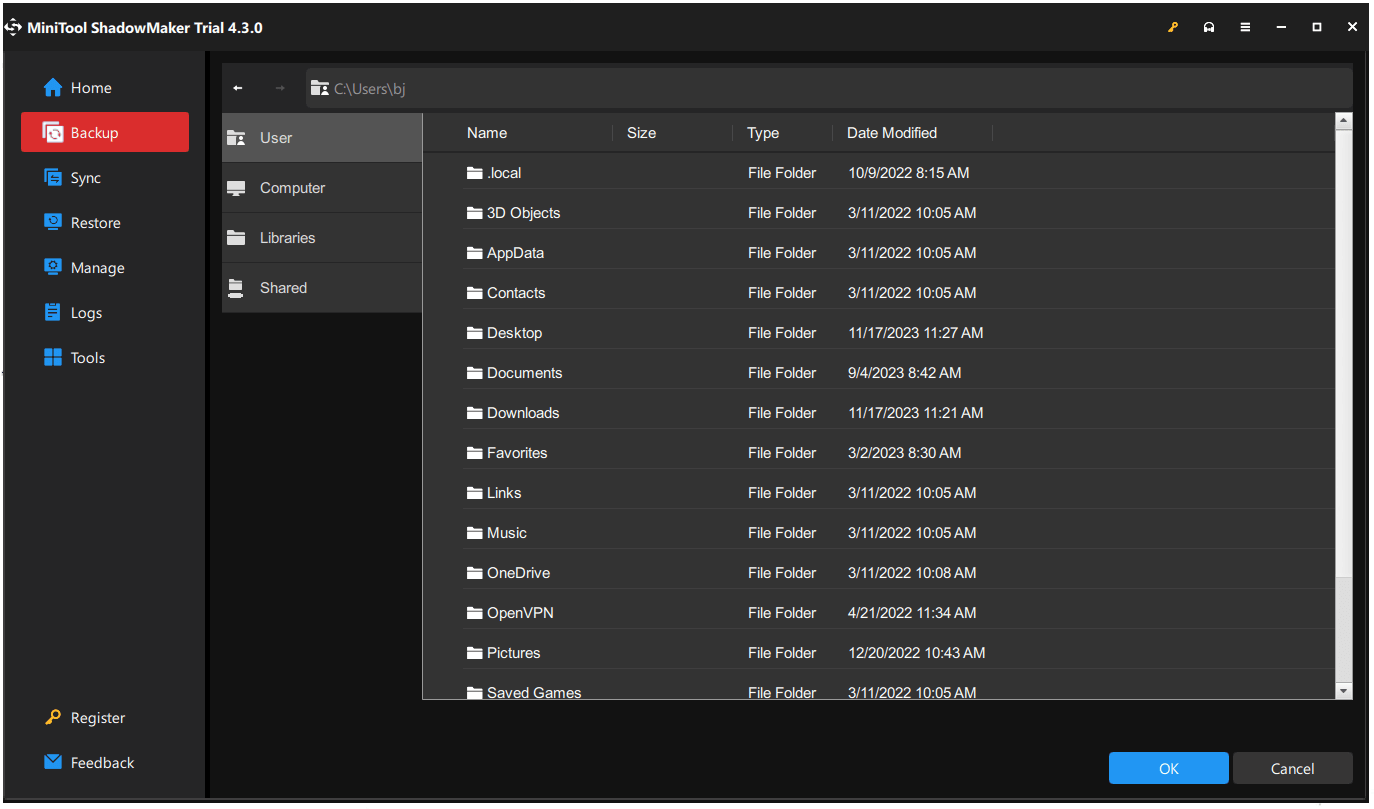
Step 3: Then you click the Options feature to configure the backup settings and click Back Up Now to start it immediately after everything has been set.
Tip 5: Regularly Change and Create Strong Passwords
You’d better change your password regularly and use a stronger password, such as some special symbols and different number plus word combinations. Do not use some numbers related to your personal information, such as birthday or phone number, which is easy to deduce.
Tip 6: Use Secure Wi-Fi
Some people are used to connecting to some unknown Wi-Fi in public when they are working in a café. It is not safe at all. Any device can get infected by connecting to a network and this public Wi-Fi can be easily hacked unwittingly. You need to be careful.
Bottom Line:
What is a cyber-attack? After reading this post, you may have an overall picture of cyber-attacks. This full guide is useful to help you distinguish different types of cyber-attacks and find the right way to prevent them.
Faced with the rising cyber security issues, the first and foremost thing you should do is prepare a backup plan for your important data. MiniTool ShdowMaker is what we recommend. If you have any issues with this tool, you can contact us via [email protected].

