This article will illustrate you the meaning of disk defragmentation and the reasons for the appearance of disk fragments.
By using the system software or professional disk defragmentation software, we can arrange the fragments and messy files in our computer. This process mentioned above is called disk defragmentation. It can improve the overall performance and the running speed of a computer.
Disk fragments or file fragments are produced in the process of saving files scattered to different parts of the whole disk rather than in a continuous clusters. After a period of time, due to the repeated writing and deleting, free sectors in disks will be spread to discontinuous parts of the disk. Thus the files can not be saved to continuous sectors. When reading and writing, the head will move back and forth, which will slow down the disk access speed.
Why Disk Fragments Appear
Main Reasons
When the required physical memory is not enough (please go to this page if you encounter not enough disk space error when you plan to upgrade/update Windows 10), most of the operating systems will bring out temporary file on the hard disk, and the space occupied by this file will be virtualized to memory. And the virtual memory management program will do frequent reading and writing operation to the hard disk, and then there will be a lot of fragments in the hard disk.
Other Reasons
When browsing on the Internet, some temporary files or settings in temporary file directory will be generated by Internet Explorer or other browsers. Then massive fragments will be found in the system. File fragmentation does no damage to the system, but it will reduce the disk performance. What’s more, it will even shorten the disk’s service life.
Ways to Manage
1. Using disk defragment program in Windows 7.
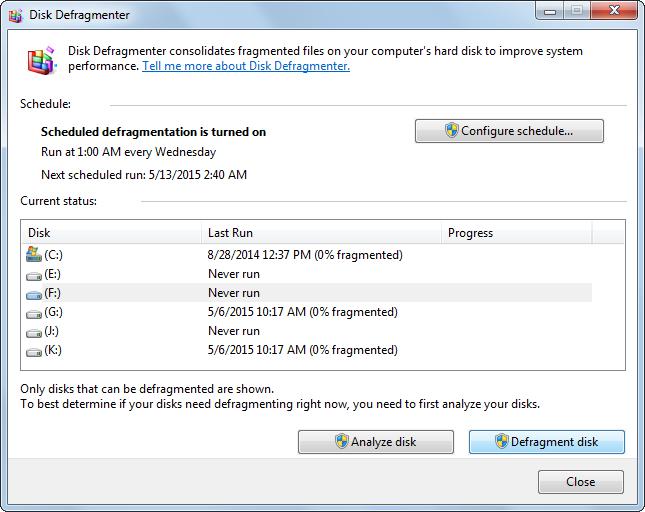
Start “Search programs and files” to input Disk Defragmenter > Click “Disk Defragmenter” > Click the volume that you want to defragment > Click “Defragment Disk”.
2. Relying on some disk defragment tools.
Make Recommended Settings to Reduce Fragments
Settings on Optimization
Users have two choices which are called fast optimization and complete optimization. Home users can choose fast optimization (once every half a year). Optimizing is to move the frequently used files to the high performance area in a drive to fasten the reading speed.
Setting of Files Gap
We recommend that users should not keep file gap. If we reserve the setting, a large number of fragments will be produced.
Move Catalogue Close to MFT
This move will greatly fasten the file reading speed.
Related Common Sense
Disk defragmentation should be run in the following situations.
- After increasing a lot of documents in the computer;
- There is only about 15% available free space in the disk;
- Installed a new program or the new version of Windows.
Linux’s File System
Linux file systems can be roughly divided into two blocks: the inode region and the block region. There are many records in the inode. And each record is used to store the information, including permission, modificated date, name, etc. The actual content of a file may be scattered in different locations in the block. The position information is recorded in a record of the inode. Block area is a serial of fixed block. And it is responsible for the actual content of the document. Inode functions like index, and the block is data area.
Comparison Between Linux and Windows
When reading a file in Linux:
- Searching the corresponding file in the inode area.
- Get the conclusion that the files’ location in different blocks.
- Design the best route to get (read) these blocks in hard disk.
When reading a file in Windows:
- Find the corresponding files in the distribution list, and read the first cluster.
- Move to the next cluster and read according to the clusters’ position.
- Repeat operations in step 2 until the file is over.
If the file on the disk is fragmented, Windows needs doing more operations to find these files while the Linux can read in order at a time. For Windows, saving file continuously is good to improve the efficiency of reading.