What Is ReFS File System
Which one comes to your mind at first when talking about the file system? NTFS, FAT32 or exFAT? Here is a question: Do you know what resilient file system (ReFS) is?
The Resilient File System (ReFS) is the latest file system released by Microsoft, aiming to maximize data availability, scale efficiency to large data sets across diverse workloads and offer data integrity to the damaged resiliency. It is also designed to resolve a series of expanding storage scenarios and lay a solid foundation for innovation in the future.
ReFS is the new file system made up from the current NTFS file system code. However, it is not the replacement of NTFS, it has its own merits and demerits instead. More importantly, it is able to address some major issues of NTFS.
Main Functions of ReFS
Compared with NTFS, ReFS has four main new functions. The functions mainly contain disk construction reliability, built-in resiliency, compatibility and deletion four aspects.
However, ReFS doesn’t support some functions of NTFS, such as, NTFS compression, file system encryption, hard links, disk quotas, etc. Additionally, Windows cannot boot from ReFS volume. Mirrored and stripped volumes on dynamic disks are replaced by mirrored and stripped storage pools in Storage Space. However, only the mirrored space supports automatic error-correction in ReFS.
Let’s explain the functions of ReFS one by one.
Disk Construction Reliability
ReFS allows large scalability without real limit on folders and content size (hardware limits still work). The supported maximum file size and volume size are 16 exbibytes and 1 yobibyte respectively. Free space is calculated by a layered distributor which contains large, medium and small chunks three divided tables.
Built-in Resilience
ReFS introduces a new function that can check the damage accurately and repair those damage at the same time so as to provide higher integrity and availability for data. Whenever you read or write the file, ReFS will check it to ensure that there’s nothing wrong.
What’s more, ReFS doesn’t check whether files have corruption only when reading and writing them. The data integrity scanning program will check all the files on the drive regularly to recognize and fix the corrupted data. This means the resilient file system has the internal resilience to check whether the file data is damaged. And you don’t have to use chkdsk at all.
However, if there’s no alternative copy to recover from for the corrupted data that ReFS has checked, the file system will delete the data from the drive immediately. You don’t have to restart the system or set the drive as offline as with NTFS file system.
Compatibility
ReFS only supports the “widely adopted” Win32 API which doesn’t require new system APIs, and it is used by most file system filters.
You are not allowed to format any old partitions as ReFS on Windows10. At present, you are only able to utilize ReFS with storage space and prevent data from damaging with the reliability of ReFS.
The Pros and Cons of ReFS
Just as said in earlier, ReFS has its own pros and cons. It is a wise choice to understand the advantages and disadvantages of the file system before selecting one. Look at this guide, and you will acquire what you want.
The Pros of ReFS
As the latest file system, ReFS has some advantages that others don’t have. You can take a view.
- Faster than NTFS
- In support of large size for volumes, files and content
- Data scrubbing
- Automatic integrity check
- No need to run CHKDSK
- Integrate with storage space
The Cons of ReFS
Inevitably, ReFS still has some disadvantages and needs further improvement. If those demerits are acceptable, you can use it either.
- Windows is unable to boot from ReFS.
- Compared with NTFS, ReFS consumes more system resources
- NTFS data cannot be converted to ReFS
- The larger the disk array, the more RAM and IOPS ReFS uses for file integrity
- It doesn’t support removable media, short names, transactions, object IDs, etc.
How to Use ReFS
Currently, you can use the ReFS in Windows 10 only through the storage space feature. Besides, it requires you to create a two-way mirror with two hard drives and utilize Storage Spaces in FeFS to format the storage.
Therefore, if you just want to examine how to use ReFS but you don’t have the required extra hard disk drives (two), you can use two virtual drives.
Here are steps to use ReFS, please read them carefully.
Step 1:
1.Type control panel in the search window and click it.
2.Click System and Security to continue.
3.Choose storage spaces in the pop-up page.
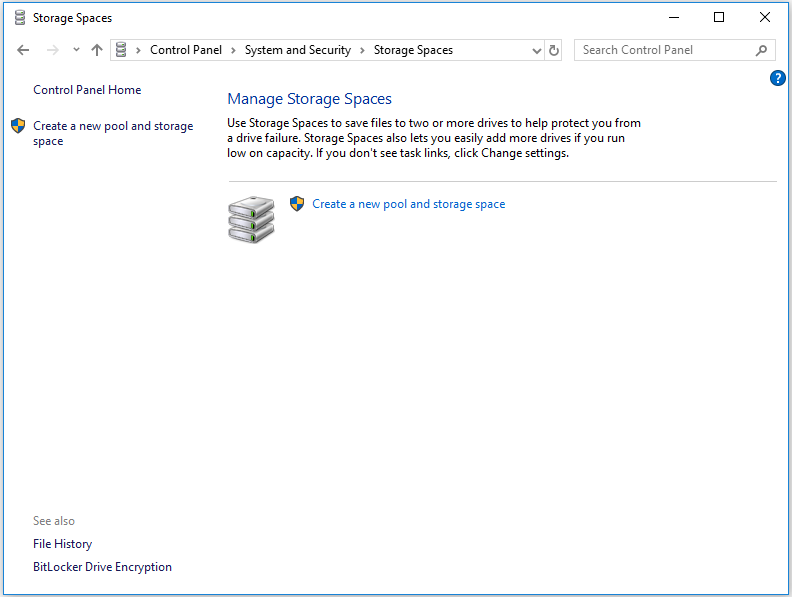
Step 2: Click Create a new pool and storage space to continue.
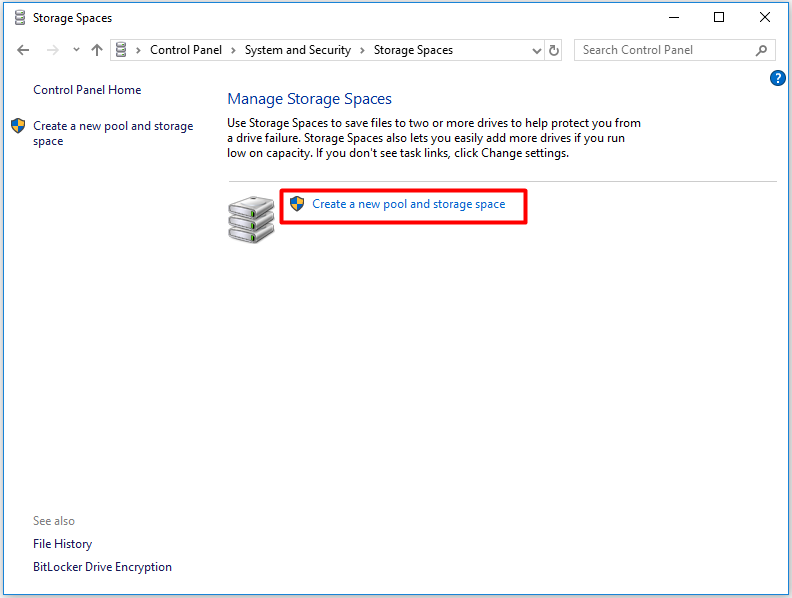
Step 3:Click Create pool. Then choose a drive letter for the pool, set the size for the pool and choose ReFS file system. After that, click create storage space to finish the process.
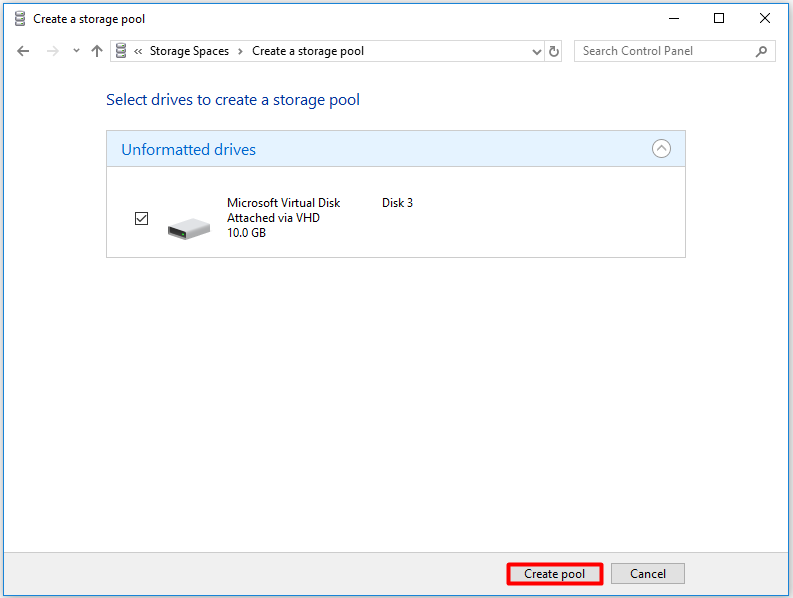
If you would like to use the data integrity feature of ReFS file system, you can choose it when you see the file system option.
You may be interested in this post if you are using the ReFS file system: New Express: Microsoft to Remove Full ReFS Support from Win10 Pro.