What is System Volume Information? It’s a folder presented by default for each drive on your computer, even the external USB devices plugged in your PC. Usually, the folder is hidden, so if you want to see it, you need to enable the option Show Hidden Items in File Explorer.
Introduction to System Volume Information
What is System Volume Information used for? In fact, it is used for storing necessary information including System Restore Points, Volume Shadow Copy, Indexing Service Database, NTFS Disk Quota Settings, Distributed Link Tracking Service Database, DFS Replication and File deduplication service database.
However, if your drivers are formatted with the NTFS file system, then you cannot access the System Volume Information folder, even you use administrator privileges. And if you double-click the folder, you’ll receive an error message saying that “Location is not available” or “Access is denied”.
So why does this thing happen? This is because Windows uses this folder for certain system-level features. The permissions are set to protect against users and programs without the appropriate permissions amending the files inside and interfering with important system functions.
Luckily, you can open the System Volume Information folder if your drive is formatted with the exFAT or FAT32 file system. And if you open the folder, you can see that there are two files present there – WPSettings.dat and IndexerVolumeGuid.
The IndexerVolumeGuid file is used to assign a unique identifier to the drive. Then the Windows Indexing Service analyzes the drive’s files and indexes them to make you can access them faster.
Whenever a drive is connected to the computer, Windows looks for the identifier and determines which search database to query and associate with the drive. Therefore, you can use Cortana on Windows 10, the search box in the File Explorer or in the Start menu.
The WPSettings.dat file is also created by Windows service, but the function of it is not sure.
How to Reduce the Size of System Volume Information?
Is System Volume Information large? Sometimes it is. This is because it contains your system restore points. So how to reduce the size of System Volume Information? You can delete some restore points.
Here is the tutorial:
Step 1: Open Control Panel and then choose System and Security.
Step 2: Click System and then click System Protection in the left panel.
Step 3: Select the drive you want to reduce the size of the System Volume Information folder and then click Configure….
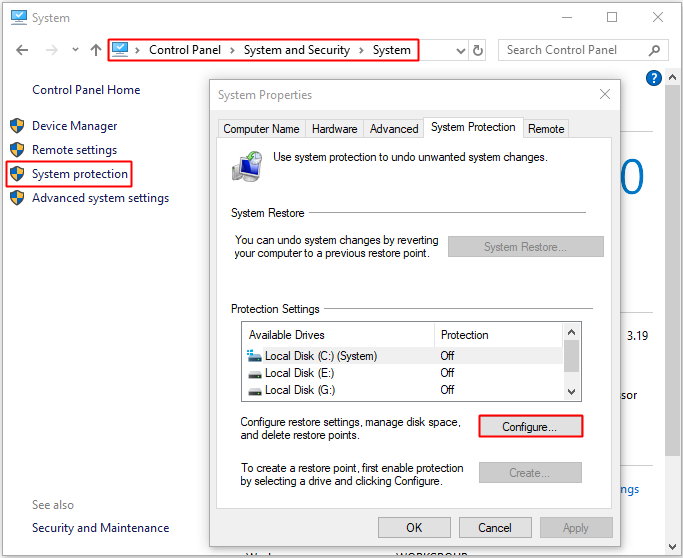
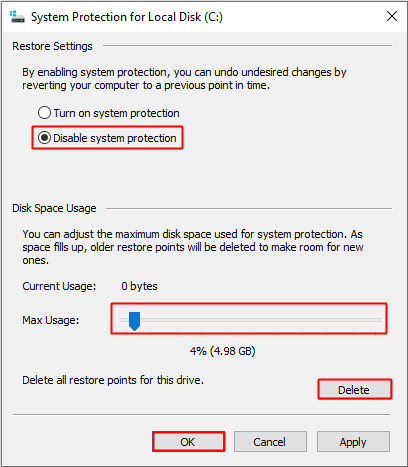
Step 4: By default, the System Restore can take up to 10 GB space for system restore per drive, which means the system restore can consume 10 GB, so you can reduce the size of the System Volume Information folder by reducing the maximum space using Max usage. Then click OK to save changes.
Note: If you are sure that you don’t need the system restore points, you can click Delete to clear the previous restore points. In addition, you can also choose to check Disable system protection to disable the system restore mechanism for the drive.
Can I Delete System Volume Information?
Actually, you shouldn’t delete the System Volume Information folder. You cannot access it on NTFS-formatted drives, leave alone deleting it. However, you can delete it on exFAT or FAT32 formatted drives, Windows will recreate it again automatically. So there is no need to delete it.
What’s more, the System Volume Information folder is vital for the Windows operation and has lots of necessary functionalities. So if the folder is too large, just reduce its size according to the method mentioned above. Never try to change the permissions on the folder to delete it.
Final Words
From this article, you can know what System Volume Information is and why you cannot delete it. Besides, you can know the methods to reduce the size of the System Volume Information folder.