Have you encountered the 400 Bad Request error when visiting a website? This post from MiniTool introduces the 400 Bad Request error in detail, tells you what causes the HTTP Error 400, and shows you how to solve this problem.
What Is 400 Bad Request Error?
The 400 bad request error is an error that occurs in various browsers. When you visit a website, if the server is unable to process (understand) the request sent by the client due to incorrect request syntax, invalid request message framing, or deceptive request routing, it will throw out the HTTP error 400.
When you trigger the HTTP Error 400, Google Chrome and Microsoft Edge will tell you that, but some browsers like Safari and Firefox just display a blank page, so you don’t even know it occurs. In addition, the HTTP error code 400 also has the following variations:
- HTTP Error 400
- HTTP Error 400 – Bad Request
- HTTP Status 400 – Bad Request
- HTTP Error 400. The request hostname is invalid
- 400 Bad Request
- 400 Bad Request. Request Header Or Cookie Too Large
- Bad Request – Error 400
- Bad Request – Invalid URL
How to Fix HTTP Error 522 Connection Time Out?
What Causes the 400 Bad Request Error?
The HTTP Error 400 can be triggered for the following reasons:
- URL String Syntax Error. For example, you have typed the wrong URL; the URL contains illegal characters like “{”, etc.
- Corrupted Browser Cache & Cookies. If the browser cache files are corrupt or the browser cookies are expired/corrupt, the way the cookie handling your login authentication data may have gotten corrupted. Then, it can’t successfully authenticate you as a valid user with admin privileges and your request will be refused.
- Bad DNS Cache. The DNS data stored locally is out of sync with registered DNS information. In this case, the name resolution process can’t be completed and your request will be refused.
- File Size Too Large. Some servers have a file size limit. If you upload a very large file to these servers, you may also get the error code 400.
- Server Error. If there is something wrong with the server, you may also encounter HTTP Error 400.
How to Fix 403 Forbidden Error? Here Are 3 Fixes For You
How to Fix the 400 Bad Request Error
Now that you know what causes the HTTP Error 400, you can take corresponding measures to solve it.
#1. Check the URL Again
Please check the domain name spelling. If the URL contains a directory path, file name, or query string, pay attention to special symbols such as a hyphen (-) or percentage character (%), making sure these special characters have been encoded correctly and are legal URL characters.
If necessary, you can visit this website by searching for the title or keywords of the article or page.
#2. Clear Browser Cache and Cookies
The browser cache contains website files such as texts and images. The cookies store the user’s session history and preferences. They can make the page load faster and improve the browsing experience.
However, if they are corrupt and cause the 400 Bad Request error, you can clear them to solve the problem. If you are using Google Chrome, the process should be as follows:
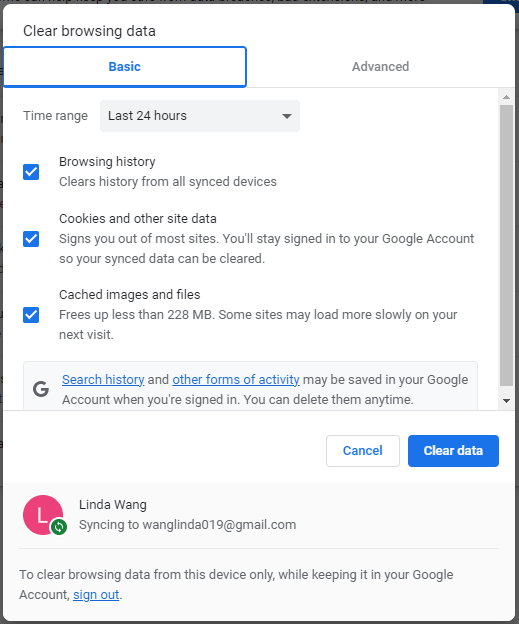
- Click on the three dots icon on the top right corner of Google Chrome and select Settings.
- Go to the Privacy and security tab and click on Clear browsing data.
- Make sure all items are selected and click Clear data.
#3. Disable Browser Extensions
Some extensions may interfere with the request sent to the web server, causing the 400 Bad Request error. Therefore, disabling browser extensions may solve the problem. If you are using Google Chrome, you can click on the three dots icon on the top right corner of Google Chrome and then select More tools > Extensions to turn off these extensions.
What Causes 500 Internal Server Error and How to Fix It
#4. Check the File Size
If the HTTP Error 400 occurs when you’re trying to upload a file to a website that’s exceeding the server file size limit, you can try uploading a smaller file to see if the error occurs again. If not, you may need to reduce the file size by compressing it or splitting it into smaller files.
#5. Flush DNS Cache
When you visit a site for the first time, the system will search for the nameservers and IP addresses that are associated with the domain name (the web server), and then store this information in the DNS cache.
Therefore, when the system visits the website again, it can reduce the DNS lookup process, making the site load faster. However, if the DNS cache becomes corrupt, the 400 Bad Request error may occur. In this case, you can clear the DNS cache to solve the problem.
On Windows PCs, you just need to open Command Prompt and execute the command “ipconfig /flushdns”.
Bottom Line
MiniTool Partition Wizard can help you clone the system, manage disks better, and recover data. If you have this need, you can download it from the official website.