Microsoft has introduced the Sudo command, a Linux feature in Windows 11. To wonder about what Sudo for Windows is and how to enable and configure Sudo command, continue reading this post and MiniTool will show many details here.
Sudo for Windows Has Come to Windows 11
On February 8, 2024, Microsoft rolled out Windows 11 Insider Preview Build 26052 to the Canary and Dev Channels. This build first introduced the new feature – Sudo for Windows, a Linux command that allows you to run programs with elevated privileges, similar to “Run as Administrator”. This feature also belongs to part of Windows 11 24H2.
According to Microsoft, if you need to run elevated commands directly from an unelevated console session, Sudo for Windows is a new way. Via it, you won’t first open a new elevated console when you want to elevate a command, which is an ergonomic and familiar solution.
Next, we will show you how to get a new Windows build, enable Sudo command in Windows 11, and configure it.
Install 26052 or Above to Get Windows 11 Sudo
To enjoy this feature, you should upgrade your Windows 11 to Build 26052 or above.
Before the upgrade, remember to back up your PC beforehand to prevent some potential issues like data loss, system crashes, etc. For PC backup, run MiniTool ShadowMaker, an excellent Windows backup software.
MiniTool ShadowMaker TrialClick to Download100%Clean & Safe
Then, go to Settings > Windows Update, check for available updates and download & install them. Or, access the Download Windows Insider Preview ISO page, download an ISO, burn it to a USB drive via Rufus, and boot the PC from the drive for a clean installation. Then, try some operations to enable and configure Sudo to use.
How to Enable Sudo Command in Windows 11
Before using Sudo for Windows, enable it firstly via Settings:
Step 1: Press Win + I to open Settings.
Step 2: Navigate to System > For developers.
Step 3: Scroll down to the Enable sudo section and switch the toggle of this option to On. Then, click Yes to confirm the operation.
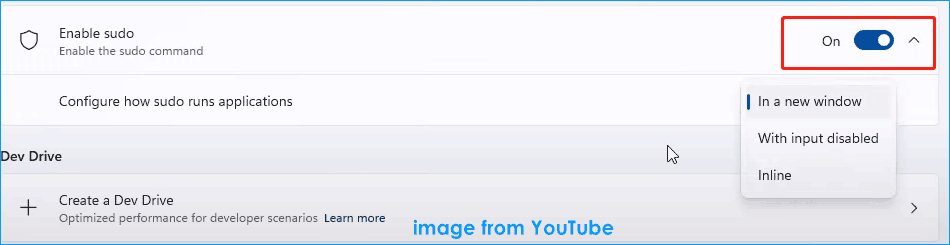
After turning this feature on, you can see the field of Configure how sudo runs applications. Three options are for you to choose, including In a new window, With input disabled, and Inline. If you don’t know how to configure Sudo for Windows, move to the next part.
How to Configure Sudo for Windows
Let’s explore three different configuration options in detail:
- In a new window: When running the Sudo command, the terminal will open a new window.
- With input disabled: Sudo for Windows will run the elevated commands in the current window, but the new process won’t accept any inputs. If you run processes that need further user input after elevation, this configuration isn’t working.
- Inline: The terminal will execute administrative tasks in the same window when running Sudo.
To configure Sudo for Windows, you should choose one option in Settings as per your needs. Alternatively, you can also do this thing via Command Prompt:
Step 1: In Windows 11, right-click on the Windows button and choose Terminal (Admin).
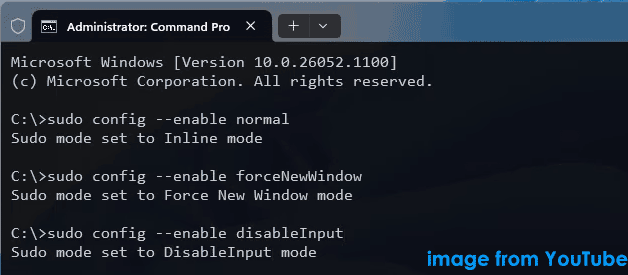
Step 2: Copy and paste one of the following commands to the window and press Enter.
sudo config –enable normal: enable Sudo Inline mode
sudo config –enable forceNewWindow: enable Sudo In a new window mode
sudo config –enable disableInput: enable Sudo With input disabled mode