About Dynamic Disk Database
Sometimes, you might want to convert your disk to dynamic disk for its greater flexibility and more useful options than basic disk. It’s true that dynamic disk is more popular than basic disk among professionals.
You can use Disk Management tool to convert your basic disk to dynamic without data loss. Just right-click the basic disk, choose Convert to Dynamic Disk from the drop-down menu, and follow the onscreen instructions to complete the process.
However, it is possible that you cannot activate Convert to Dynamic Disk feature but receive an error message: There is not enough space available on the disk(s) to complete this operation.
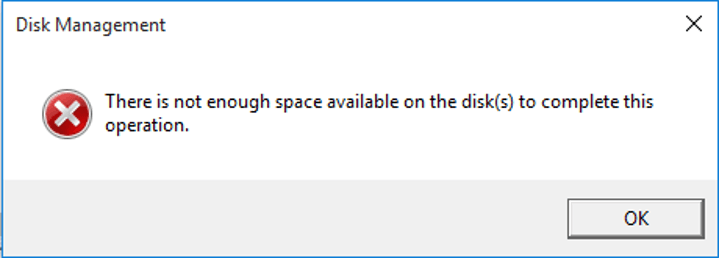
Why does this error occur? Why do you need enough free space on the disk to perform this operation?
Actually, each dynamic disk has a disk management database which is used to track information about dynamic volumes in the computer. It is critical for a dynamic disk. If there is not enough space on the basic disk for the database, you cannot convert it to dynamic disk.
How much storage does a dynamic disk require for the disk management database?
The database takes up only 1 megabyte (MB) on the disk. Besides, the location of the database is determined by the partition style (GPT or MBR) of the disk.
On a GPT disk, a chunk of disk space is reserved as the Microsoft Reserved Partition (MSR) to provide alternative data storage space. And the dynamic disk database is contained in the reserved partition. While on an MBR disk, the database is located in a 1 MB area at the end of the disk which might be occupied on the basic disk.
It is difficult for users to check the database in the reserved partition. But if you are using MBR, you can get known about whether there is 1 MB at the end of the disk. Just keep reading to get the method.
How to Know Whether There Is Enough Space for Dynamic Disk Database
When you want to check whether there is enough space at the end of the disk for dynamic disk database, the Disk Management might be your first choice on hand. However, this built-in tool can only tell you the unallocated space but provide no information about its location.
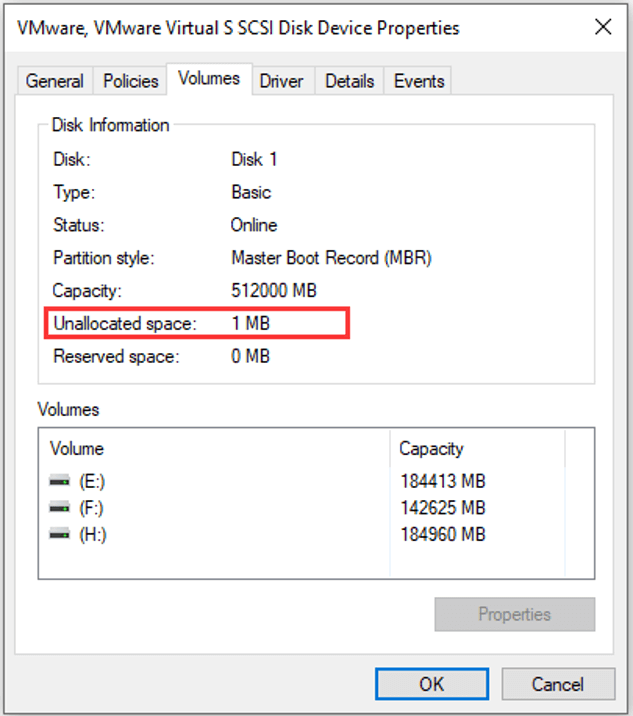
For example, the following picture shows the properties of my basic disk. Under Volumes tab, you can see that the disk has 1MB unallocated space which should have met the requirement of dynamic disk database. However, I get the same error when I convert it to dynamic disk, which indicates that this 1MB storage isn’t at the end of disk.
Hence, you may need to make use of a professional third-party program to check the required storage and its location. MiniTool Partition Wizard is recommended for you here. Just click the following button to download and install it on your computer.
MiniTool Partition Wizard FreeClick to Download100%Clean & Safe
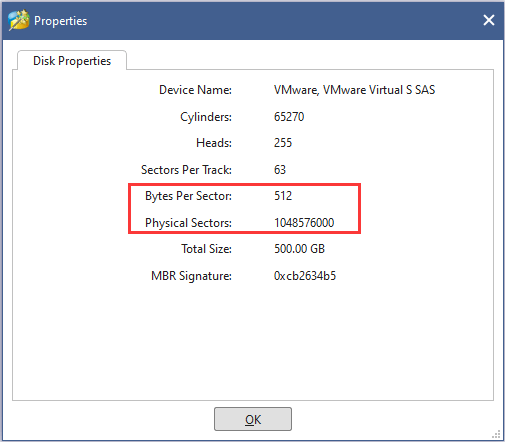
Step 1: After launching the application, right-click your basic disk and choose Properties to get the following window. Here you need to make a note of two items and their values: Bytes Per Sector and Physical Sectors.
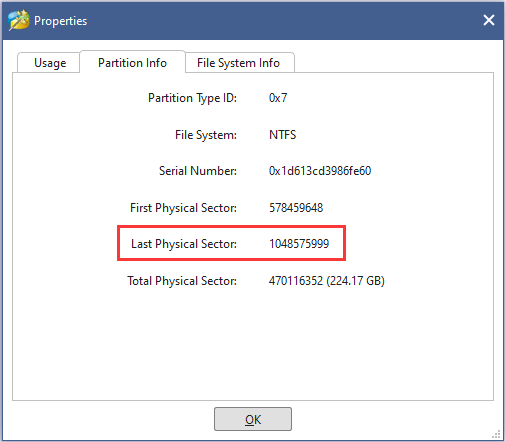
Step 2: Then, go back to the main interface, right-click the last partition on the disk and choose Properties to get the detailed information about the partition. Switch to Partition Info tab, and you can see the Last Physical Sector of the partition.
If the value of this item is less than that of Physical Sectors mentioned above, it means there is unallocated space existing at the end of the disk. And the difference of them is the number of sectors of the unallocated space.
Step 3: Now you need to figure out the size of the unallocated space. Just multiply the number of unallocated physical sectors by the value of Bytes Per Sector. The result of the multiplication is the size of the unallocated space at the end of disk. Don’t forget to convert bytes to megabytes.
If there is 1MB or more, you should be able to convert your basic disk to dynamic without problems. But if there is not enough storage for dynamic disk database, you need to take action to spare storage for it.
How to Spare Storage for Dynamic Disk Management Database
After learning about the error that might happen when you convert basic disk to dynamic and the reason for it, it’s time to get the way to fix it. Actually, to ensure there’s enough storage for dynamic disk database, you just need to shrink the last partition on the disk.
To achieve this, three methods are displayed here for you. You can choose your preferred one to shrink the partition.
Note: It is risky to shrink a partition, especially a raw partition (without a file system) that contains data, because shrinking the partition might destroy the existing data. Thus, you had better to back up the partition in advance.
Method 1: Use Disk Management
If you want to manage your partitions or disks, Disk Management is always a good choice for you. To shrink a partition in Disk Management, just follow the steps below.
Note: In Disk Management, you can only shrink partitions that have no file system or that use the NTFS file system. To get more information about file system, you can check this post. Besides, with this tool, you cannot shrink a partition beyond the point where any unmovable files are located.
Step 1: Right-click the Start button and choose Disk Management to open it.
Step 2: Right-click the last partition on the disk which you want to convert to dynamic and select Shrink Volume.
Step 3: When you get the following window, type the amount of space you want to shrink in MB in the editable box. Of course, you have to ensure there is at least 1 MB left after shrinking.
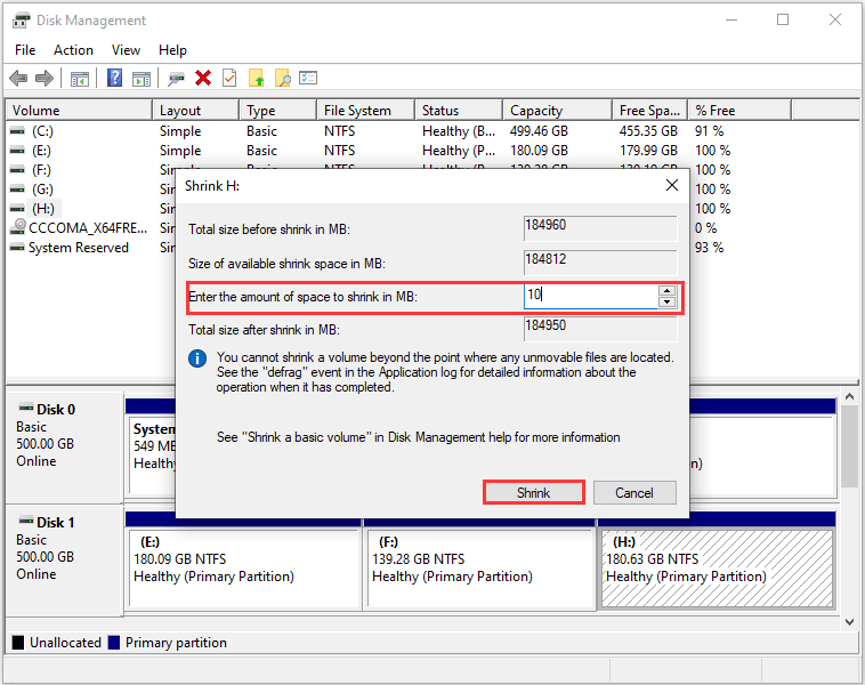
Step 4: Then, click Shrink button to confirm the operation.
After that, you can try converting the disk to dynamic right in this tool and the mentioned error will not appear again.
Method 2: Use Command Prompt
Alternatively, you can shrink the partition in Command Prompt with a few of commands. But you should know that this utility doesn’t support file systems other than NTFS, either. Here’s how to do it.
Step 1: Press Windows + R to open Run window.
Step 2: Type in cmd in the empty box and click OK to open Command Prompt.
Step 3: Input the command diskpart and press Enter to open diskpart.exe window.
Step 4: In the new window, input the following command and don’t forget press Enter after each.
- List disk
- Select disk <number>
- List partition
- Select partition <number>
- Shrink desired = # (# refers to the amount of space in MB that you want to shrink)
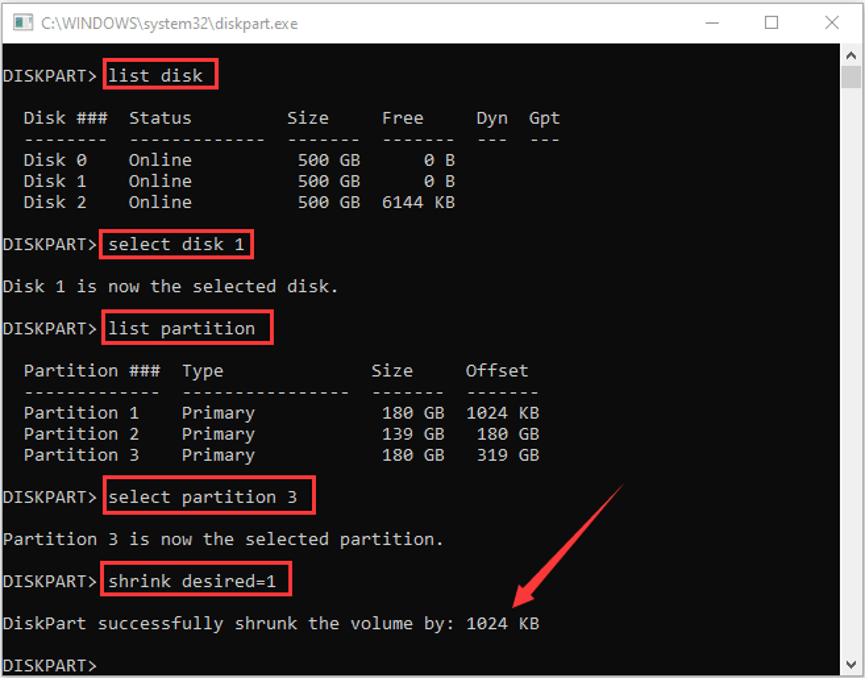
Now, you have shrunk the partition successfully. In terms of converting to dynamic disk, you can also make it in this window. You just need to execute the following commands:
- Select disk <number>
- Convert dynamic
Method 3: Use MiniTool Partition Wizard
As you can see, the tools built in your computer introduced above can only help you shrink the partition with specific file system. Thus, if you want to perform the operation for partition with other file systems such as FAT32, you have to ask a third-party program for help.
You can continue using MiniTool Partition Wizard to make it. Just refer to the following tutorial:
Step 1: Launch MiniTool Partition Wizard to get its main interface.
Step 2: Select the partition which needs to be shrunk and choose Move/Resize Partition from the left tool bar.
Step 3: In the pop-up window, drag the right triangle leftward to leave enough space for the dynamic disk database at the end of disk. Then, click OK button to go back to the main interface.
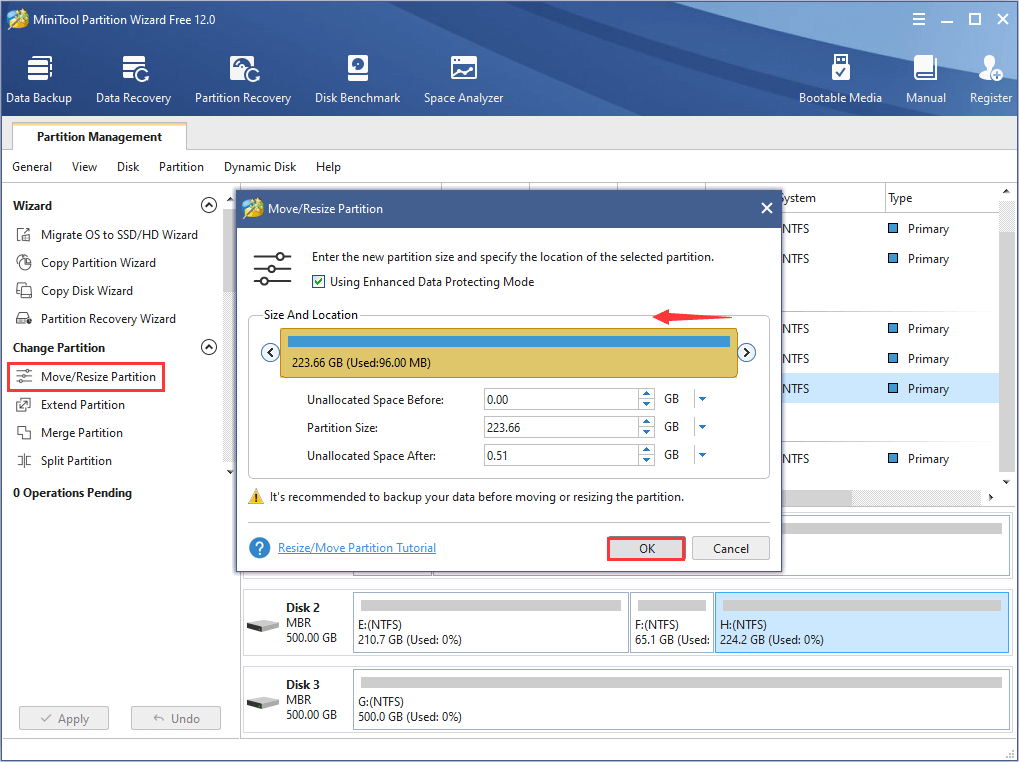
Step 4: Click Apply button to confirm the operation.
Differences Between Basic and Dynamic Disk
Basic and dynamic disks are two forms of volume management.
Basic disk is the most common storage type used in Windows operating system and it uses a partition table to keep track of all partitions. It supports creating two types of partitions, namely primary partitions and logical drives, to manage contiguous unallocated space on the same MBR disk.
While dynamic disk offers more flexibility than basic disk, as it uses a hidden logical disk manager (LDM) or virtual disk service (VDS) to track information about the dynamic volumes. It allows volumes to have noncontiguous extents on one or more dynamic disks, and supports creating volumes with fault tolerance like mirrored volume.
Do you want to learn more about basic and dynamic disk? Click here to see the comparison between them.
How to Convert Dynamic Disk to Basic Disk
For personal reasons, you might want to convert dynamic disk to basic, which is more complicated than converting to dynamic.
You can use Disk Management tool and Command Prompt to achieve this, but you have to delete all the volumes on the dynamic disk. So, if you want to complete the conversion without data loss, using a professional third-party program is your only choice.
MiniTool Partition Wizard also provides this feature and you can have a try. Besides, it is a paid feature so you need to buy the license to activate it.
After entering the main interface, just right-click the target disk and choose Convert Dynamic Disk To Basic Disk or select the feature from the left pane. Then, click Apply to execute the operation.
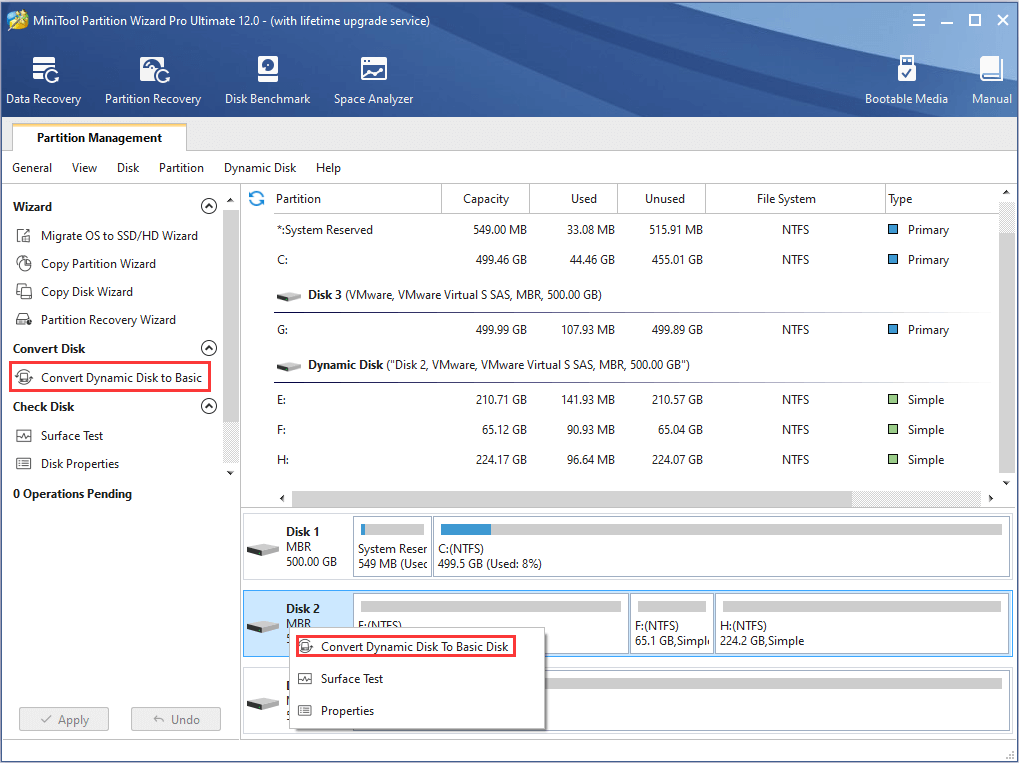
Bottom Line
This post has introduced dynamic disk management database, and provided the ways to fix not enough space available to convert to dynamic disk. Hope you can benefit from this post.
If you have any questions about this post or when you using MiniTool Partition Wizard, please leave a message in the comment section below. You can also contact us via [email protected].
How Much Storage for Dynamic Disk Database FAQ
Dynamic disk has many features that basic disk doesn’t have. It allows you to create volumes containing noncontiguous extents on one or more disks, so it offers higher flexibility than basic. Besides, it saves a copy of the database which can be used to repair the damaged database, which is known as fault-tolerance.
But it also has disadvantages. For example, it’s not supported on portable computers or Windows XP Home Edition-based computer.