What Is QEMU
QEMU, short for Quick Emulator, is a free open-source hosted virtual machine manager that can execute hardware virtualization. With the help of KVM (Kernel-based Virtual Machine), QEMU can offer fast running speed. Therefore, it develops fast and is going to replace VirtualBox and VMware on Linux.
However, on Windows, the advantages of QEMU are not significant, because the KVM technology is not applicable on the Windows host machine. In addition, the quickgui is also not available to Windows. But QEMU develops fast and many people still want to use this VM software on Windows.
QEMU for Windows Download and Install
1. Download QEMU for Windows
To use QEMU for Windows, you should download and install it first. Please refer to the following QEMU download guide:
Step 1: Go to the official QEMU website (https://www.qemu.org). Click the Download button at the top section. You will go to the QEMU download page.
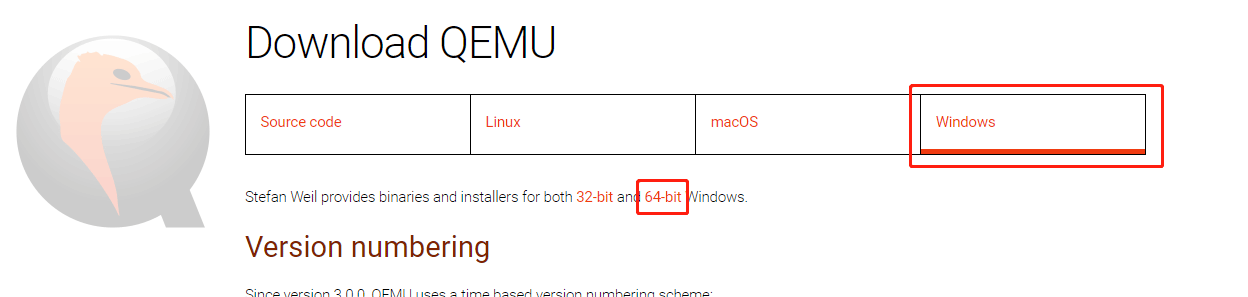
Step 2: Click the Windows tab to get the QEMU Windows version. Click 32-bit or 64-bit according to what OS you are running (for me, I click the 64-bit because my OS is 64-bit).
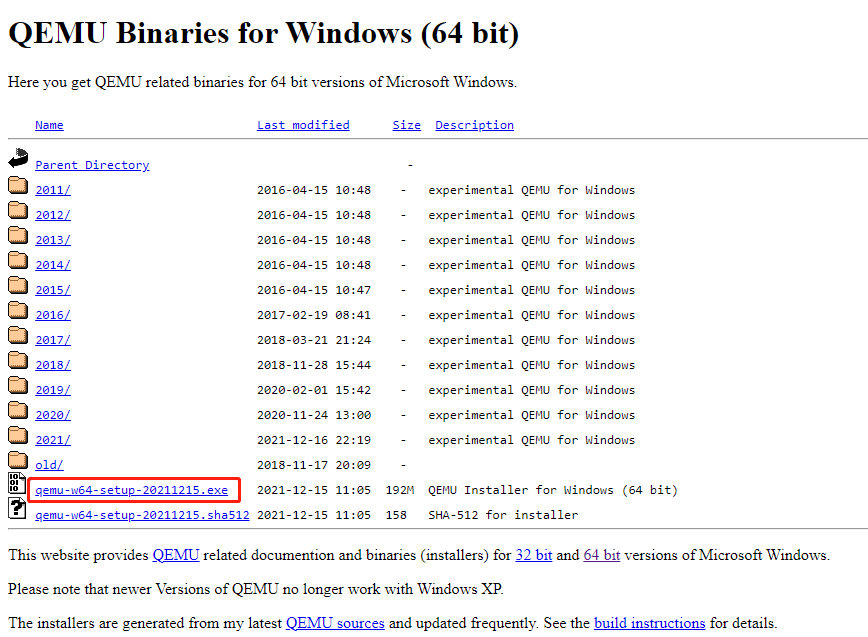
Step 3: On the new page, click the .exe file to download it. This file is the installer file.
2. Install QEMU for Windows
After the installer file is downloaded, you can double-click it to run directly. Before doing that, I recommend you to create a partition separately for it. For any virtual machine software, I will recommend you create a separate partition to store the software and the VM files so that you can manage them better.
To create a separate partition, you can use the shrink feature in the Windows Disk Management tool. But this tool can’t help you move the location of partitions, so I recommend you to use MiniTool Partition Wizard.
If the free space of one partition is not enough, you can move/resize another partition to get more unallocated space and then gather the unallocated space together to create one partition. Here is the guide:
MiniTool Partition Wizard FreeClick to Download100%Clean & Safe
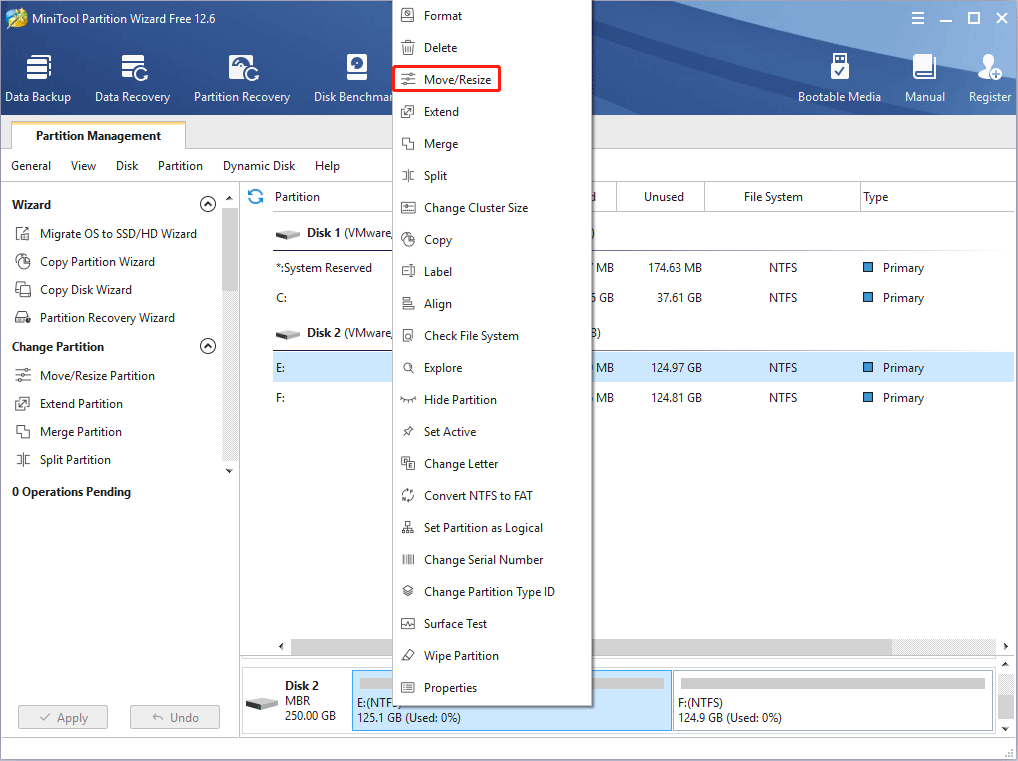
Step 1: Launch MiniTool Partition Wizard and go to its main interface. Right-click a partition and choose Move/Resize.
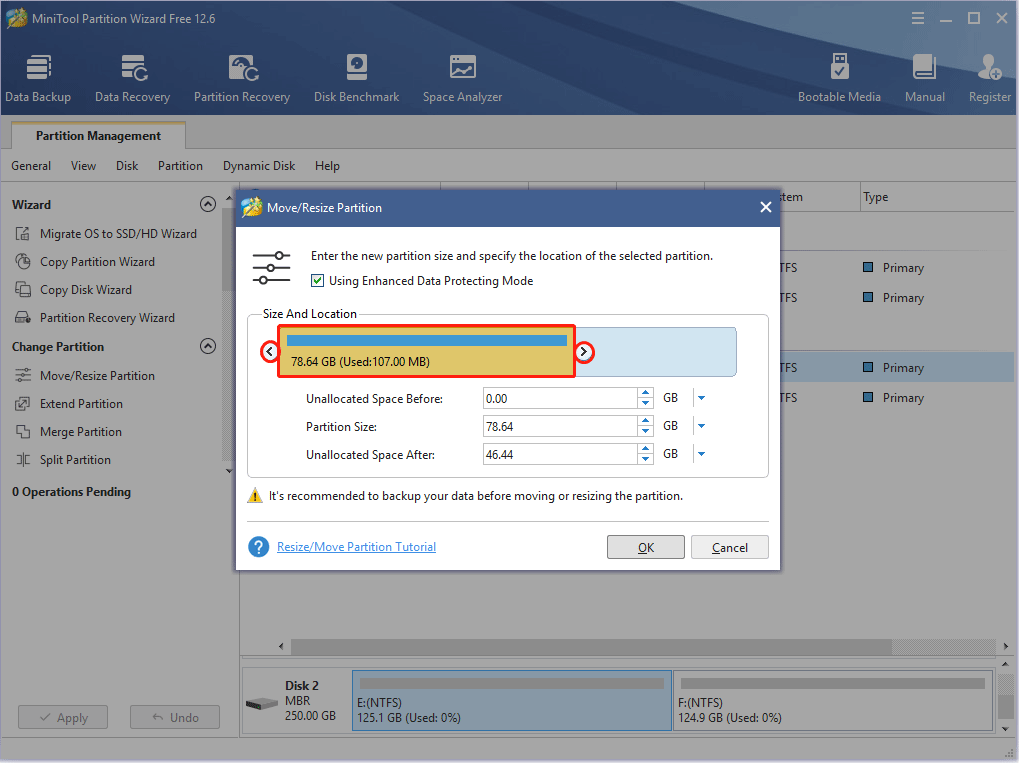
Step 2: Drag the two arrows on the two sides of the partition to shrink the partition, and then drag the block to move the location of the partition. Then, click the OK button. In this way, you can get unallocated space.
Step 3: Right-click the unallocated space and choose the Create button.
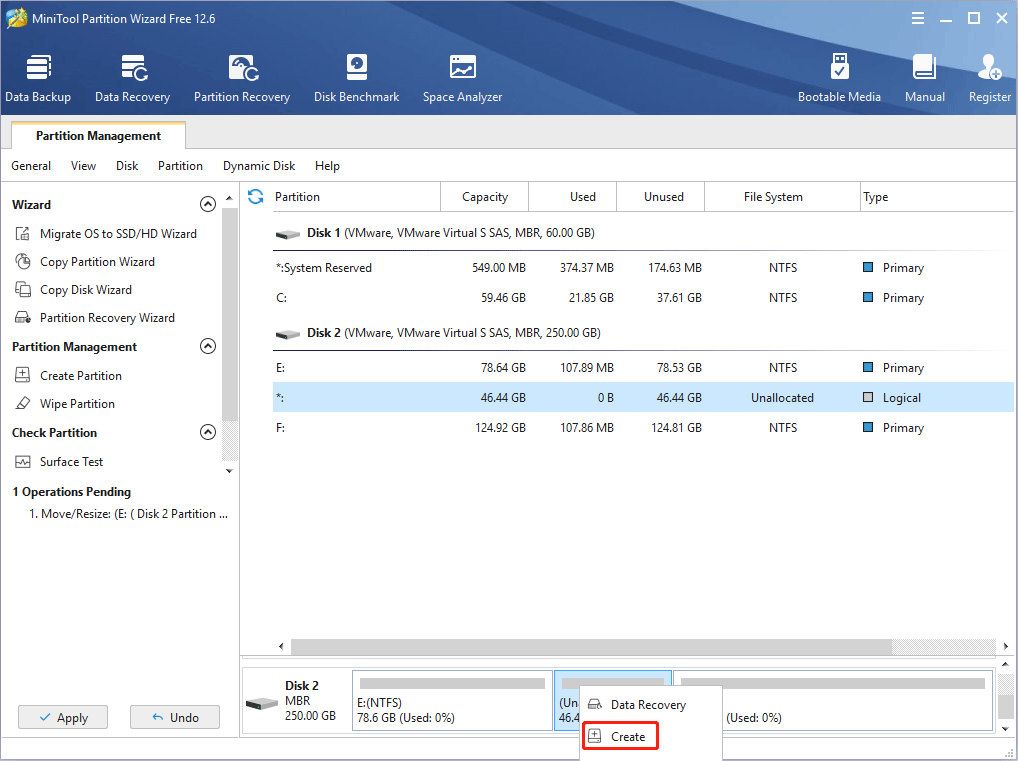
Step 4: Set parameters for the new partition. You can keep all of them to the default value if you don’t have specific demands. Then, click the OK button.
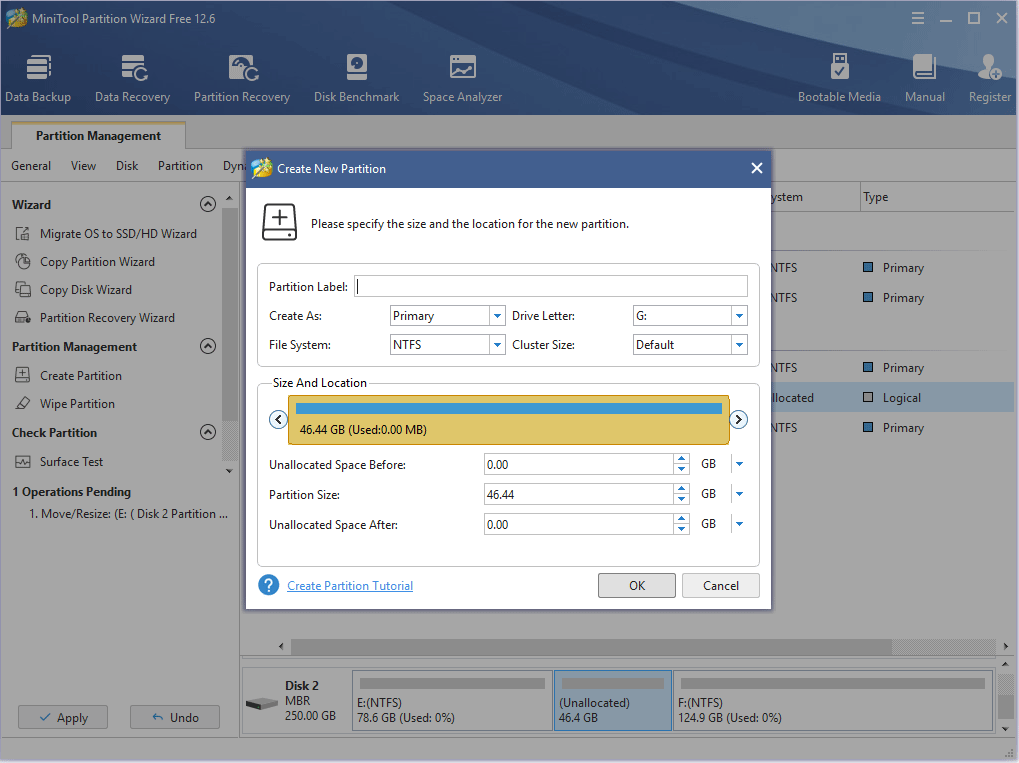
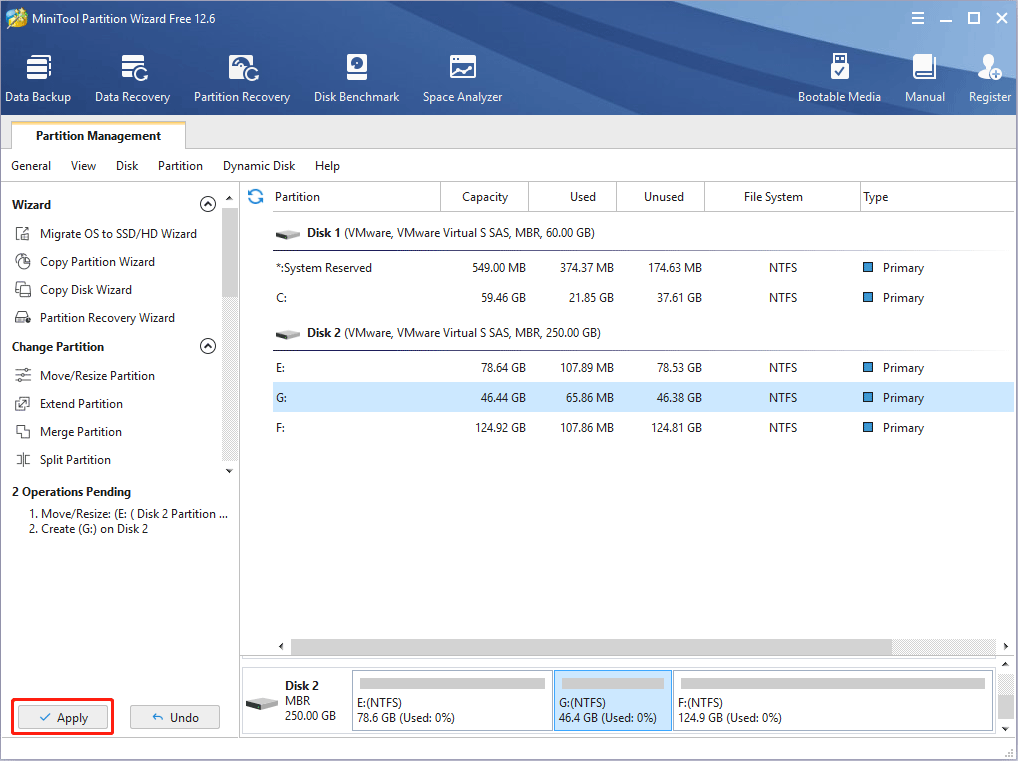
Step 5: Click the Apply button to execute pending operations.
How to Merge Unallocated Space in Windows 10 for a Large Drive
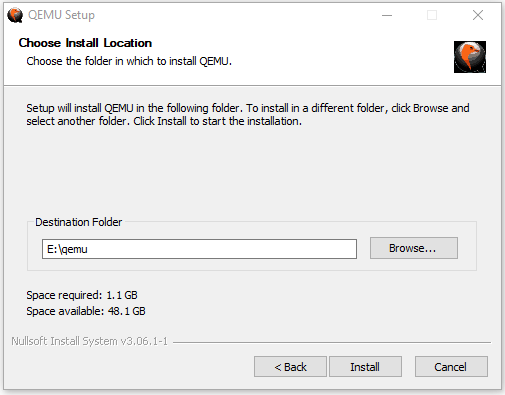
After the new partition is created, you can then double-click the QEMU installer file to install this VM software. You just need to follow the on-screen instructions to complete the installation.
How to Use QEMU on Windows
After installing the QEMU Windows version, you may want to know how to use QEMU to create a virtual machine. Here are 2 ways and the 2nd way is better.
Way 1. Create a Virtual Machine Using Commands
QEMU doesn’t come with a GUI. If you don’t install a GUI manually, you need to use commands to run QEMU. Here is the guide on how to use QEMU on Windows to create a VM via commands (taking Ubuntu as an example).
Step 1: Download the Ubuntu ISO file from the official website.
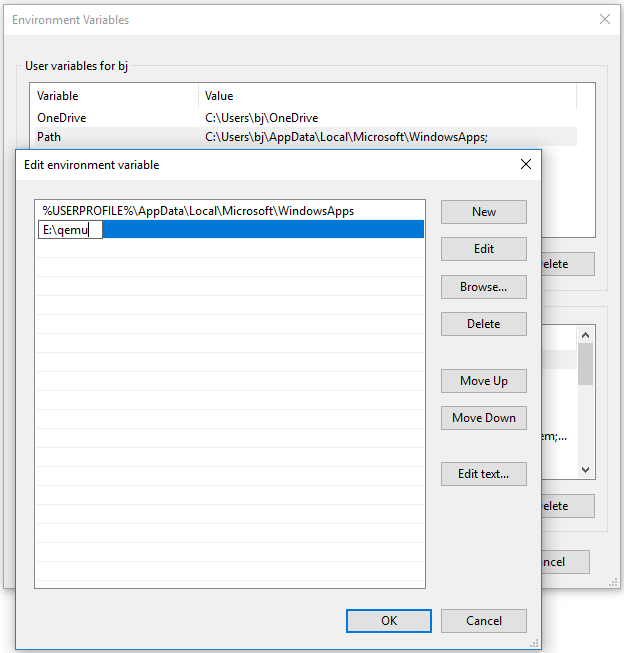
Step 2: Add QEMU path into Environment Variables.
- Open File Explorer, go to the QEMU installation location, and then copy the path (E:\qemu).
- Right-click This PC / Computer, choose Properties, and then click Advanced system settings.
- Under the Advanced tab, click Environment Variables.
- In the User variables box, double-click the Path variable, click New, and then paste the QEMU path.
- Click the OK button to save changes, and then click the OK button again to save and exit the Environment Variables
1. If you use Windows 7, the adding process may be a little different.
2. If there is no Path variable under the User box, you can create one, or you can add the QEMU path into the System variables.
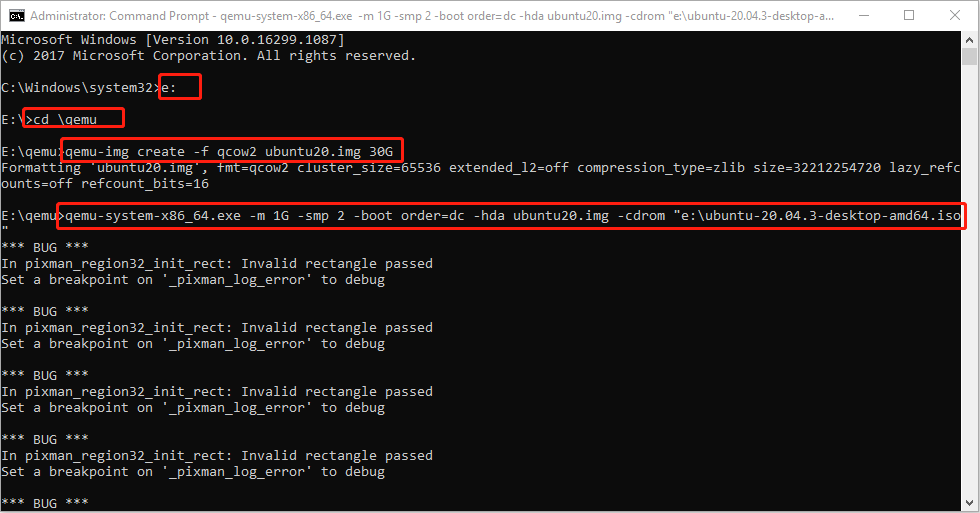
Step 3: Run Command Prompt as administrator and then execute the following commands.
- E: (this will open the e drive where QEMU is installed).
- cd \qemu (this will open the qemu folder).
- qemu-img create -f qcow2 ubuntu20.img 30G (this will create a virtual hard drive of 30GB).
- qemu-system-x86_64.exe -m 1G -smp 2 -boot order=dc -hda ubuntu20.img -cdrom “e:\ubuntu-20.04.3-desktop-amd64.iso” (this will run Ubuntu using CD/ROM).
1. If you want to install other VMs (macOS, ARMs, etc.), the qemu-system may vary greatly.
2. The above commands are not perfect. If you have better commands, you can run them.
3. The QEMU installation path and the location of the Ubuntu ISO file in the above commands should be changed accordingly.
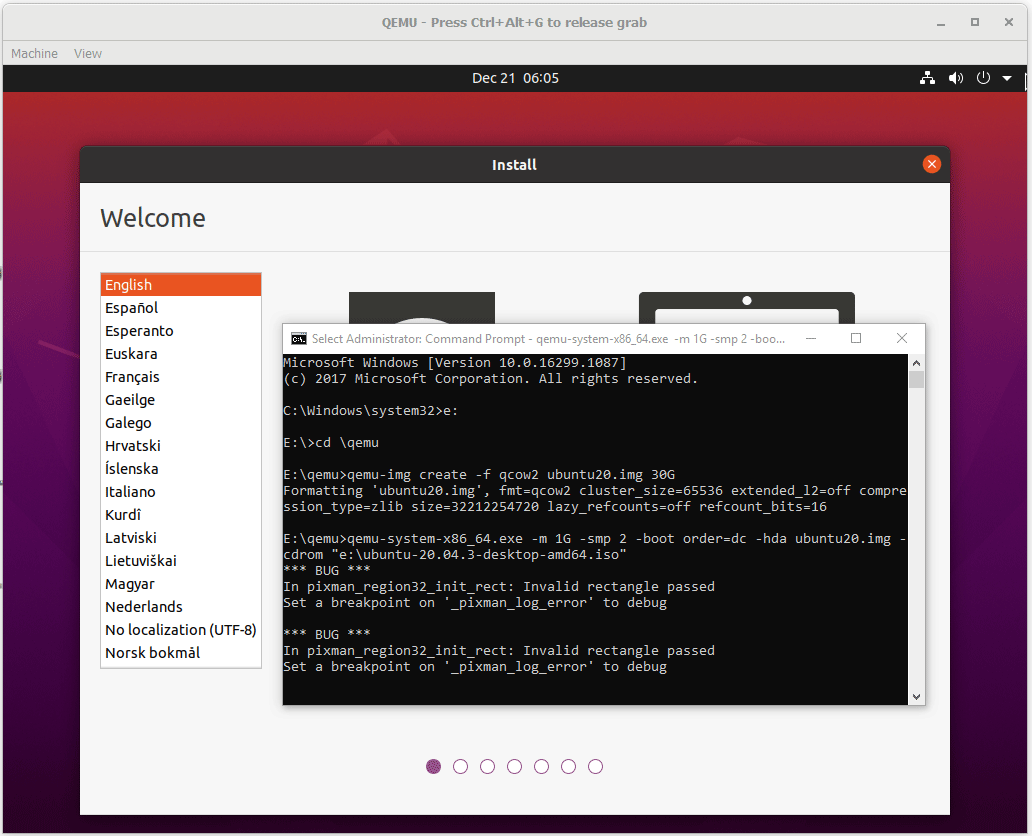
Step 4: Go through the Ubuntu installation process. Although there may be many bugs, I launch Ubuntu 20 successfully and then just need to complete the installation process.
How to Install Linux (Ubuntu) on Windows 10 [Ultimate Guide 2022]
Way 2. Create a Virtual Machine Using QtEmu
As you can see, creating a VM using QEMU via commands is a tough job. You need to search for various tutorials online. In addition, once errors occur, you may have no idea how to solve them. Therefore, I recommend you to use QtEmu, an open-source GUI for QEMU Windows.
How to use QEMU on Windows via QtEmu? Here is the guide:
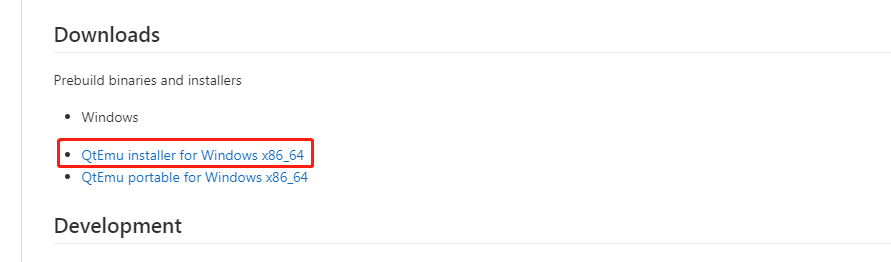
Step 1: Download the Ubuntu ISO file and QtEmu. The QtEmu official website is https://qtemu.org and the QtEmu source is placed on https://gitlab.com/qtemu/gui. Go to the GitLab source page, scroll down to find the Downloads section, and click the first link to download the QtEmu installer.
Step 2: Double-click the QtEmu installer file and go through the installation process. When you are asked to specify the installation location (where to create the QtEmu folder), please install the QtEmu under the QEMU folder. For me, I type: E:\qemu\QtEmu.
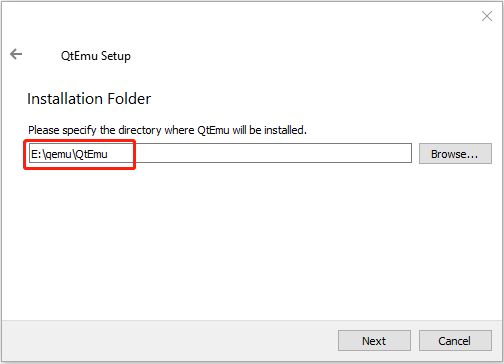
Step 3: After QtEmu is installed, go to E:\qemu\QtEmu. Right-click the qtemu.exe file and choose Send to > Desktop (create shortcut). Then, create a folder named VMs under the E drive to store all VM files to be created.
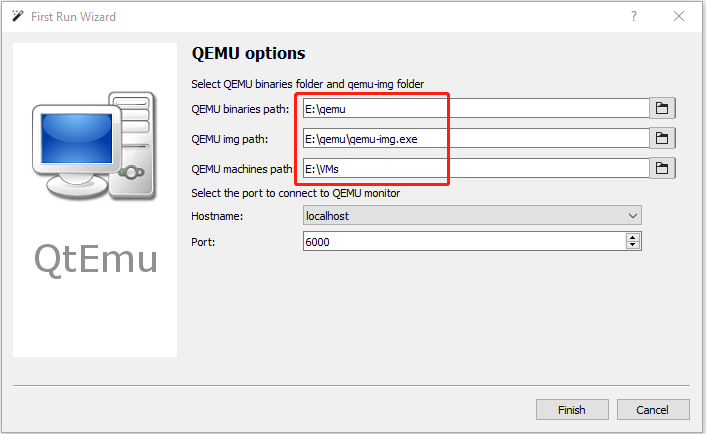
Step 4: Double-click the QtEmu shortcut to launch this software. In the QEMU options window, please set QEMU binaries path to E:\qemu, set QEMU img path to E:\qemu, and set QEMU machines path to E:\VMs. Then, click the Finish button.
Step 5: Click Machine > New Machine. Then, give a name to the new machine (Ubuntu20), choose OS type (GNU/Linux), choose OS version (Ubuntu), and then click Next.
Step 6: On the Filter page, if you don’t need to specify certain motherboard chipsets, you can click the Next button directly to skip this step.
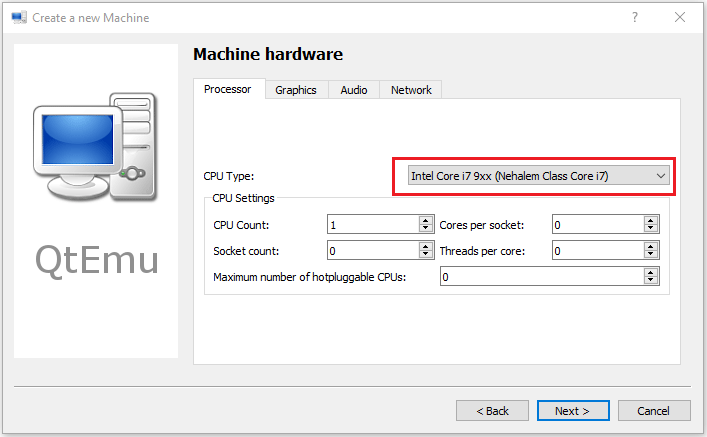
Step 7: Select a correct CPU Type, and set CPU, Graphics, Audio, and Network parameters. If all is OK, click the Next button.
What Is the Difference Between 32 Bit and 64 Bit (x86 vs x64)
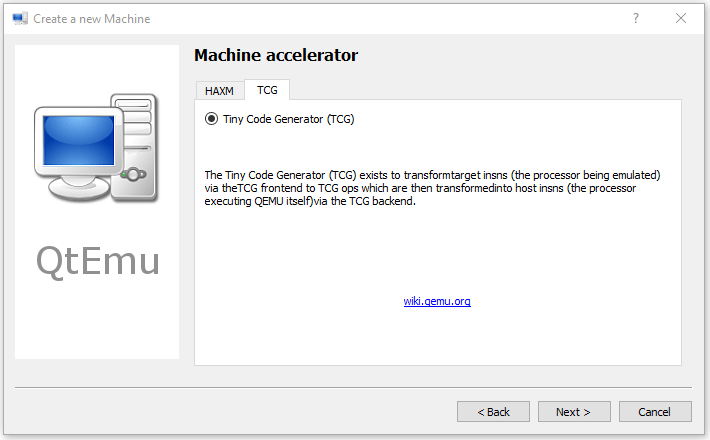
Step 8: Select the machine accelerator. HAXM is chosen by default. However, some computers may not support this technology. Therefore, I recommend you uncheck HAXM and then choose TCG instead. Then, click Next.
Step 9: Follow the on-screen wizard to set memory size, create a new virtual hard disk, set disk size and type, and then check the VM summary.
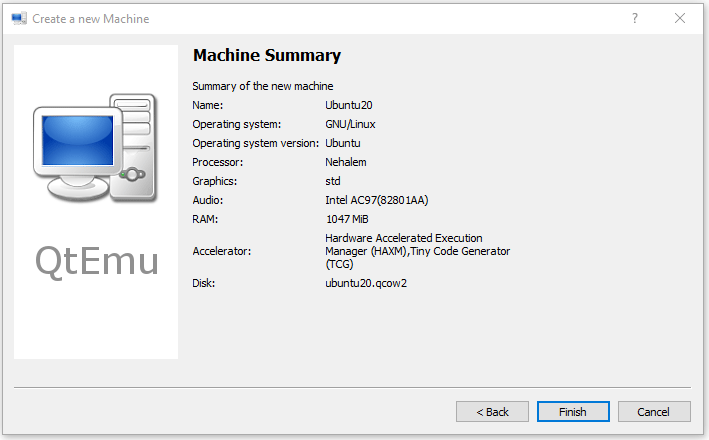
Step 10: Right-click on the newly-created VM and choose Machine Settings. Go to the Boot options tab, and tick CDROM.
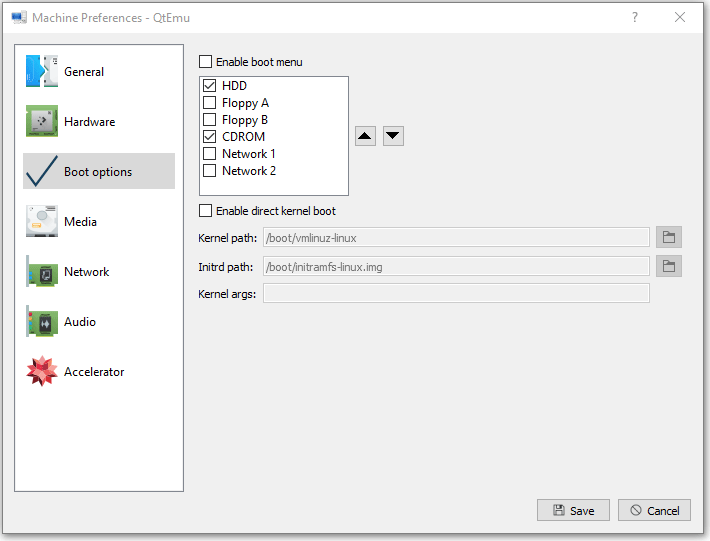
Step 11: Go to the Media tab, click the disc icon, and select the Ubuntu ISO file. Then, click Save.
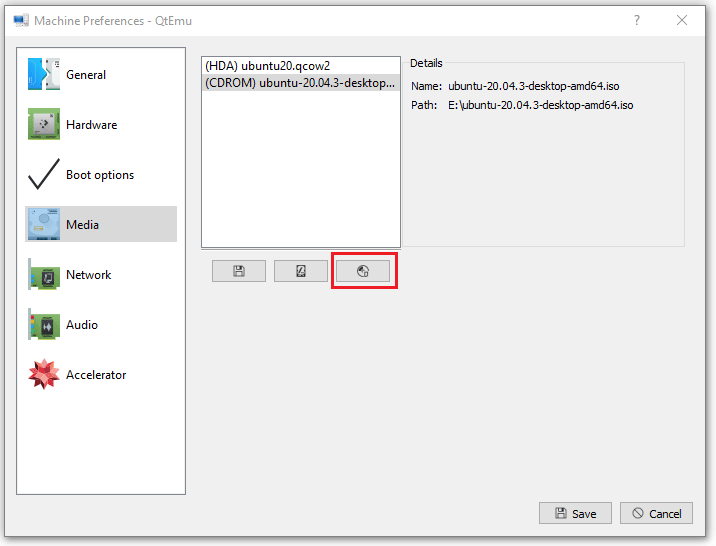
Step 12: Select the VM and then click the Play icon. Then, you may need to go through the Ubuntu installation process. After the installation process is completed, you can enjoy the VM.
Best Virtual Machine for Windows, Linux, and Mac Systems
Bottom Line
Is this post helpful to you? Do you have other ideas about how to run QEMU on Windows? Please leave a comment in the following zone for sharing. In addition, if you have difficulty in moving or resizing partitions, please feel free to contact us via [email protected]. We will get back to you as soon as possible.