A Brief Introduction to Windows Reserved Storage
Reserved storage is a feature enabled by default on Windows. Your system reserves about 7 GB of storage space, and it varies mainly depending on the Windows optional features applied and the number of languages installed. This reserved disk space is mainly used for Windows updates, applications, temporary files, and system cache to ensure the smooth operation of the system.
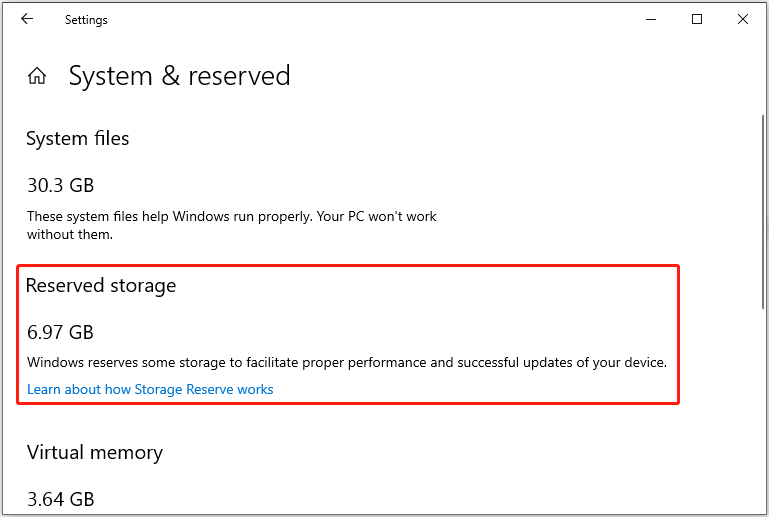
To be specific, Windows updates can occupy the reserved disk space to download and install update files. Temporary files generated when applications are running or installed will also be stored in the reserved space first to ensure fast system responsiveness. In addition, some important tasks are less likely to fail due to insufficient storage space.
Should You Enable the Reserved Storage?
Whether to keep the Windows reserved storage enabled or disable it depends on your specific needs and device situation, and it is not the same for everyone. Enabling reserved storage is mainly to avoid Windows update failure or system performance degradation due to insufficient storage space on the device. Therefore, if your disk space is extremely sufficient, you may consider turning this feature off.
How to Enable Reserved Storage Windows 10/11
If you have disabled the reserved storage and want to enable it again, you can use the following ways.
Way 1. Through Registry Editor
This is the easiest way to enable the reserved storage. Follow the steps below.
Step 1. Right-click the Start button and choose Run. Type regedit in the text box and press Enter to open Registry Editor.
Step 2. When you see the UAC window, select the Yes option.
Step 3. Copy and paste the following location to the top address bar and press Enter.
Computer\HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\ReserveManager
Step 4. In the right panel, double-click on the ShippedWithReserves option, and then set up its value data to 1. After that, click OK to save this change.
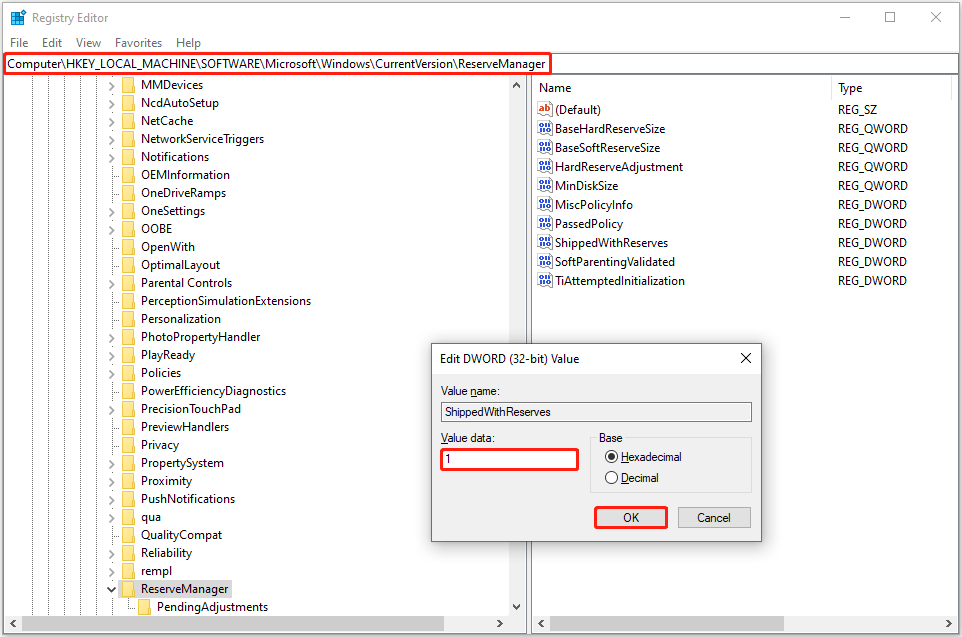
If you want to disable reserved storage Windows 10 in the future, you can change the value data of ShippedWithReserves to 0.
Way 2. With Command Prompt
If you are familiar with command lines, you can use Command Prompt to enable reserved storage. Here are the major steps.
Step 1. In the Windows search box, type cmd. When the Command Prompt option appears, click Run as administrator under it.
Step 2. In the UAC window, select Yes to continue.
Step 3. Type DISM /Online /Set-ReservedStorageState /State:Enabled in the new window and press Enter. Once this command line is completed, the reserved storage should be enabled.
You can use this command to check the status: DISM /Online /Get-ReservedStorageState.
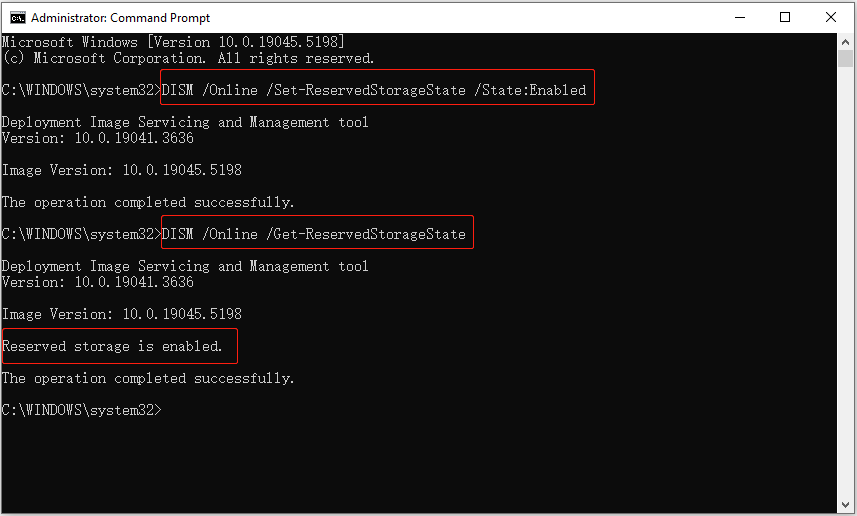
The command line to disable reserved storage is DISM /Online /Set-ReservedStorageState /State:Disabled.
Way 3. From Windows PowerShell
Alternatively, you can use Windows PowerShell to enable the reserved storage. Follow the instructions below to complete this task.
Step 1. Right-click the Start button and choose Windows PowerShell (Admin).
Step 2. Select Yes in the UAC window.
Step 3. Input Set-WindowsReservedStorageState -State Enabled and press Enter to enable reserved storage.
Suppose you need to disable that feature, just type Set-WindowsReservedStorageState -State Disabled and press Enter.
MiniTool Power Data Recovery FreeClick to Download100%Clean & Safe
Bottom Line
How to enable reserved storage in Windows 10 manually? The three ways listed above are all helpful. You can choose the one you prefer to enable this feature.